Learning objectives
- Describe the general pathology of coronary artery disease
- Describe the risk factors for coronary artery disease
- Manage patients with coronary artery disease
Definition & mechanisms
- Coronary artery disease or ischemic heart disease is characterized by obstruction of oxygen supply to the cardiac muscle
- Results in a range of complications, including myocardial infarction, dysrhythmias, heart failure, deteriorating ventricular function, and sudden death
- May also coexist with other cardiac pathologies, including valvular lesions and cardiomyopathies
- Atheromatous disease remains the most common cause
- Ischemia results when myocardial oxygen demand increases beyond supply or when there is a rupture of a plaque which can precipitate thrombosis and result in complete occlusion of an artery
Risk factors
| Unmodifiable | Advancing age |
| Male gender | |
| Family history of premature coronary artery disease | |
| Premature menopause | |
| Ethnicity (e.g. higher in those from the Indian subcontinent) | |
| Modifiable | Smoking |
| Diabetes mellitus | |
| Hypertension | |
| Obesity | |
| Sedentary lifestyle |
|
| High cholesterol (specifically a high ratio of low- to high-density lipoprotein) |
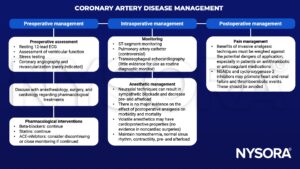
Management
Suggested reading
- Pollard BJ, Kitchen, G. Handbook of Clinical Anaesthesia. Fourth Edition. CRC Press. 2018. 978-1-4987-6289-2.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us at customerservice@nysora.com