Learning objectives
- Signs and symptoms of pneumonia
- Management of pneumonia
Definition and mechanisms
- Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the alveoli in one or both lungs
- The alveoli may fill with fluid or pus causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, and difficulty breathing
- Caused by bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae), bacteria-like organisms (Mycoplasma pneumoniae), viruses, or fungi
- Can also be caused by aspiration of food, fluids, vomit, or saliva
- Can be mild to life-threatening
- The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia
Signs and symptoms
General symptoms
Symptoms of bacterial pneumonia Symptoms of viral pneumonia Symptoms of viral pneumonia
- Chest pain when breathing or coughing
- Confusion /changes in mental awareness
- Cough, which may produce phlegm
- Fatigue
- Fever and sweating
- Lower than normal body temperature
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Shortness of breath- High fever (up to 40.5 C)
- Cough with yellow, green, or bloody mucus
- Tiredness (fatigue)
- Rapid breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heart rate
- Sweating or chills
- Chest pain and/or abdominal pain, especially with coughing or deep breathing
- Loss of appetite
- Bluish skin, lips, or nails (cyanosis)
- Confusion or altered mental state- Symptoms similar to bacterial pneumonia
- Dry cough
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Extreme tiredness or weaknessBabies and newborns may not show any symptoms of pneumonia or their symptoms may be different from adults, including:
- Fever, chills, general discomfort, sweating/flushed skin
- Cough
- Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing (tachypnea)
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Lack of energy
- Restlessness or fussiness
Signs in babies and young children include:
- Grunting sound with breathing or noisy breathing
- A decreased amount of pee or diapers that are less wet
- Pale skin
- Limpness
- Crying more than usual
- Difficulty feeding
Classification
- Pneumonia is most commonly classified by where or how it was acquired:
- Community-acquired pneumonia
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Healthcare-associated pneumonia
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia
- It may also be classified by the area of the lung affected:
- Lobar pneumonia
- Bronchial pneumonia
- Acute interstitial pneumonia
Risk factors
- Children < 2 years of age
- Adults > 65 years of age
- Hospitalization – ICU – long-term care facility
- Chronic disease: asthma, COPD, or heart disease
- Smoking
- Pregnancy
- Weakened or suppressed immune system: HIV/AIDS
- Neurological conditions making swallowing difficult: dementia, Parkinson’s disease, or stroke
Complications
- Bacteremia or sepsis
- Difficulty breathing, requiring a ventilator
- Pleural effusion
- Lung abscess
Prevention
- Vaccination: pneumococcal vaccine, flu, COVID-19
- Practice good hygiene
- Do not smoke
Diagnosis
- Medical history
- Physical exam
- Blood tests
- Chest X-ray
- Pulse oximetry
- Sputum test
- CT scan
- Arterial blood gas test
- Pleural fluid culture
- Bronchoscopy
Management
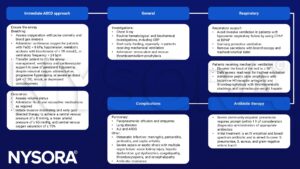
Be aware that:
- Anesthesia can contribute to postoperative pneumonia by causing gastric contents like stomach acid to enter the lungs, resulting in pulmonary complications and increased risk of infection
- Pulmonary infections and pneumonia are the most common cause of pulmonary ARDS
Suggested reading
- Morgan, A., Glossop, A., 2016. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. BJA Education 16, 167–172.
- Sadashivaiah, JB., Carr, B., 2009. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. Continuing Eduction in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 9;3:87-91.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com