Learning objectives
- Description and four degrees of uterine inversion
- Signs and symptoms of uterine inversion
- Management of uterine version
Definition and mechanisms
- Uterine inversion is a rare complication when the uterine fundus collapses into the endometrial cavity, turning the uterus partially or completely inside out
- A life-threatening obstetric emergency as it can lead to severe blood loss, shock, and even maternal death
- In extremely rare cases (5% of uterine inversions), fibroids or tumors cause uterine inversion
- Four degrees of uterine inversion:
- 1st degree (incomplete): the fundus is within the endometrial cavity
- 2nd degree (complete): the fundus protrudes through the cervical os
- 3rd degree (prolapsed): the fundus protrudes to or beyond the introitus
- 4th degree (total): both the uterus and vagina are inverted and protrude outside the body
- Time of occurrence:
- Acute: within 24 hours of delivery
- Subacute: more than 24 hours but less than four weeks postpartum
- Chronic: ≥ 1 month postpartum
- The incidence ranges from 1 in 3500 to 20,000 deliveries
Signs and symptoms
- Postpartum bleeding
- Abdominal pain
- A smooth, round mass protruding from the cervix or vagina
- Urinary retention
- Hypotension
- Hemodynamic shock
- Bradycardia
Causes
- Mismanagement of the third stage of labor such as:
- Fundal pressure
- Excess cord traction during the third stage of labor
- Other natural causes can be:
- Uterine weakness
- Precipitate delivery
- Short umbilical cord
- It is more common in multiple gestations than in singleton pregnancies
Risk factors
- Short umbilical cord
- Rapid or prolonged labor and delivery
- Use of uterine relaxants
- Nulliparity
- Fetal macrosomia
- Retained placenta
- Severe pre-eclampsia
- Uterine atony
- Placenta accreta spectrum
- Uterine anomalies or tumors (leiomyoma)
Complications
- Major hemorrhage
- Multi-organ damage
- Shock
- Sheehan syndrome
- Hysterectomy
Diagnosis
- Clinical findings
- Ultrasound examination shows an abnormal uterine fundal contour with a homogenous globular mass within the uterus
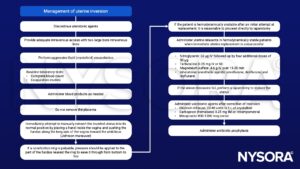
Management
Suggested reading
- Macones G. 2022. Peurperal uterine inversion. Up to date.
- Wendel MP, Shnaekel KL, Magann EF. Uterine Inversion: A Review of a Life-Threatening Obstetrical Emergency. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2018;73(7):411-417.
- Shepherd LJ, Shenassa H, Singh SS. Laparoscopic management of uterine inversion. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2010;17(2):255-257.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us [email protected]