Learning objectives
- Define orthotopic liver transplantation
- Understand the considerations of patients with a previous liver transplant
- Manage patients with a liver transplant liver undergoing nontransplant surgery
Definition and mechanisms
- Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease (ESLD) and acute liver failure
- Orthotopic liver transplantation is the most common technique and involves the substitution of a diseased native liver with a normal liver (or part of one) taken from a deceased or liver donor in the same anatomic position as the original liver
- Recipients may present for nontransplant surgery later in life
Considerations
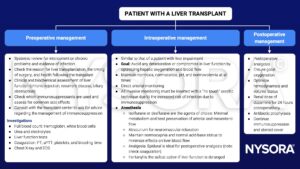
- The majority of recipients are 30-60 years old and in good health
- Cardiopulmonary effects of ESLD reverse shortly after transplantation
- Most patients have normal liver function unless there is rejection, sepsis, or recurrence of the original disease
- High incidence of hypertension after liver transplantation
- Immunosuppression increases susceptibility to infection and other common side effects
- Corticosteroids: Hypertension, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, adrenal suppression
- Tacrolimus: Hypertension, renal dysfunction, electrolyte abnormalities, hyperglycemia
- Cyclosporine: Nephrotoxicity and hyperkalemia, hepatotoxicity, neurotoxicity, hypertension
- Azathioprine: Bone marrow suppression
Management
Keep in mind
- Increasing numbers of patients have a successful liver transplant and may require nontransplant surgery later in life
- Careful preoperative assessment is essential, especially for liver and kidney function
- The goal of perioperative management is to avoid any factors that might compromise hepatic and renal function and to minimize the infection risk with antibiotic prophylaxis and careful aseptic techniques
Suggested reading
- Pollard BJ, Kitchen G. Handbook of Clinical Anaesthesia. 4th ed. Taylor & Francis group; 2018. Chapter 4 Gastrointestinal tract, Jackson MJ.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com