Learning objectives
- Definition, diagnosis, and management of hypokalemia
Definition
- Hypokalemia is a reduced level of potassium (K+) in the blood
- Serum potassium < 3.5 mmol/L
- Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms
- Life-threatening symptoms usually occur at concentrations < 2.5 mmol/L
Signs and symptoms
- Gastro-intestinal:
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Gastrointestinal paralysis
- Neuromuscular:
- Paresthesias
- Muscle cramps
- Ascending paralysis of the extremities (quadriplegia)
- Respiratory failure
- Cardiac:
- Heart failure
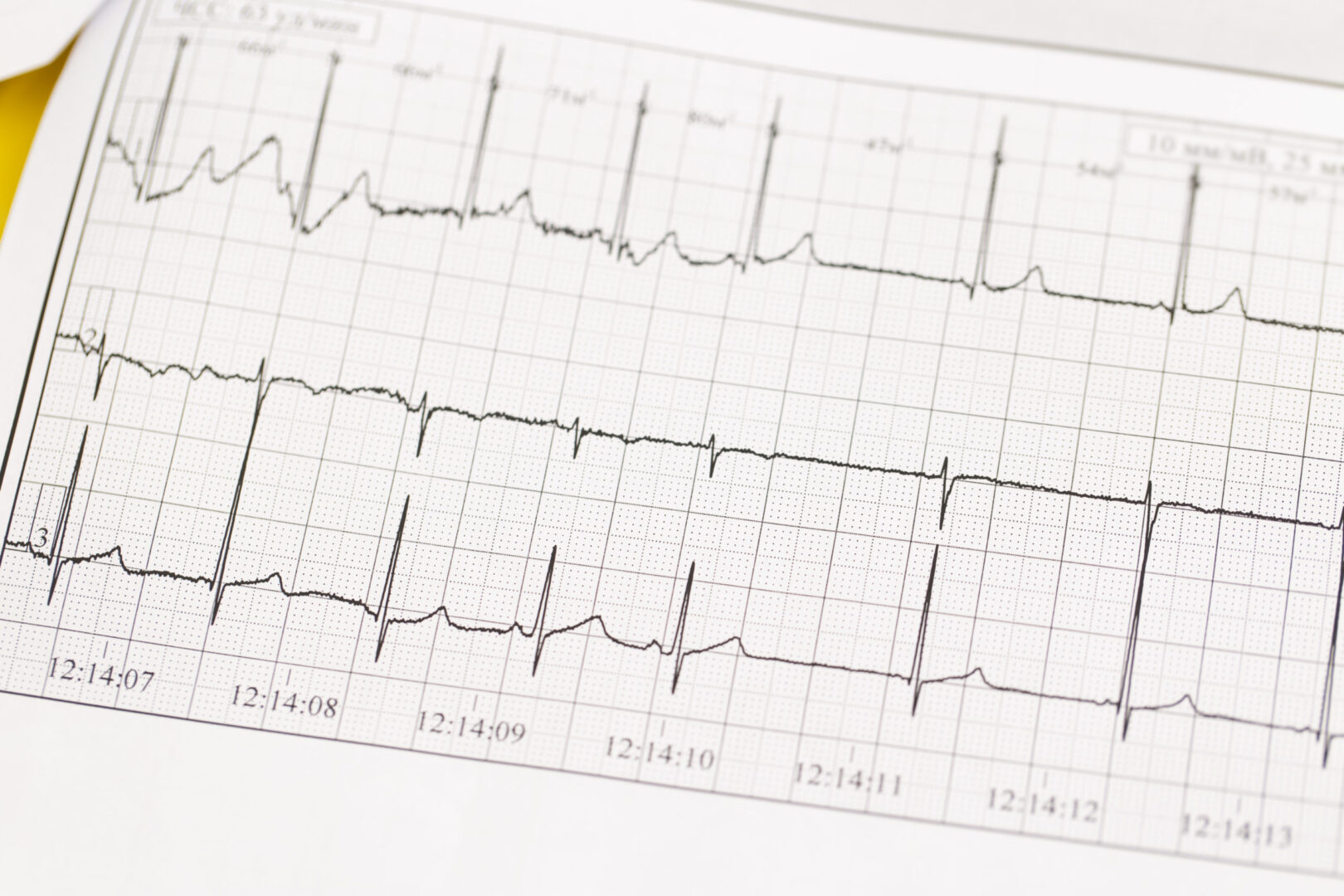
- Progressive ECG changes
- Depressed ST segment
- Diphasic T wave
- Prominent U wave
Causes
| Gastrointestinal loss | Chronic diarrhea |
| An intracellular shift of K+ | Due to insulin administration or excessive insulin secretion |
| Renal loss | |
| Cushing’s syndrome | |
| Primary Hyperaldosteronism | |
| Rare syndromes | Bartter syndrome Gitelman syndrome Liddle syndrome |
| Hypomagnesemia | |
| Medications | Diuretics (thiazides, loop-, and osmotic diuretics) Laxatives Beta-2-agonists (albuterol, terbutaline) Amphotericin B Antibiotics (carbenicillin and penicillin in high doses) Theophylline |
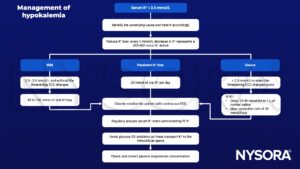
Management
Suggested reading
- Kardalas E, Paschou SA, Anagnostis P, Muscogiuri G, Siasos G, Vryonidou A. Hypokalemia: a clinical update. Endocr Connect. 2018;7(4):R135-R146.
- Viera AJ, Wouk N. Potassium Disorders: Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia. Am Fam Physician. 2015;92(6):487-495.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us [email protected]