Learning objectives
- Definition of panhypopituitarism
- Management of panhypopituitarism
Definition and mechanisms
- A rare condition in which the pituitary there’s a deficiency in all of the hormones produced by the pituitary gland
- The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland produces:
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotropin)
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Growth hormone (GH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Prolactin (PRL)
- Thyroid stimulation hormone (TSH)
- The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland produces:
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)/vasopressin
- Oxytocin
- Can affect anyone at any age
- It can be life-threatening, especially if significant deficiencies of ACTH are present, and affects 4 people per 100,000 people
- Panhypopituitarism is a type of hypopituitarism
- A deficiency or lack in one or multiple of the hormones produced by the pituitary gland
- Patients with hormonal deficiencies present with the following:
- ACTH deficiency – adrenal insufficiency
- TSH deficiency – hypothyroidism
- Gonadotropin deficiency – hypogonadism
- GH deficiency – difficult to thrive and short stature in children, adults are usually asymptomatic; however, they may feel fatigued and weak
- ADH deficiency – diabetes insipidus presenting with polydipsia and polyuria
Signs and symptoms
- Symptoms depend on the hormones depend on which hormone is deficient
- Growth problems (in children)
- Obesity
- Hair loss
- Bradycardia
- Hypoglycemia
- Hypotension
- Fatigue
- Nausea or dizziness
- Depression and/or anxiety
- Frequent infections
- Sensitivity to cold
- Unusually dry skin
- Unexplained weight loss or weight gain
- Dyslipidemia
- Tachycardia
- Excessive thirst and urination
- Female and male infertility
- Additional symptoms specific to infants, children, or adolescents
- Prolonged jaundice in newborns
- Micropenis
- Slowed growth
- Delayed puberty
Causes
| Pituitary-related | Hypothalamus-related |
|---|---|
| Pituitary adenoma Infection Injury Pituitary gland surgery Radiation therapy Pituitary apoplexy Congenital (related to midline craniofacial defects) Kallman syndrome Idiopathic | Traumatic brain injury Brain surgery Tumors such as craniopharyngiomas Secondary metastasis Pressure from hydrocephalus Stroke Tuberculous meningitis |
Complications
- Adrenal crisis (acute cortisol insufficiency) which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Weakness
- Confusion
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Hypoglycemia
- Secondary diseases:
- Obesity
- Increased cholesterol
- Metabolic syndrome
- Estradiol deficiency potentially leads to osteoporosis
Diagnosis
- MRI
- CT
- Hormone level tests:
- Blood tests
- ACTH-stimulation test
- Growth hormone stimulation test
- Insulin tolerance test
- Modern combined test
Treatment
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Pituitary surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Corticosteroids
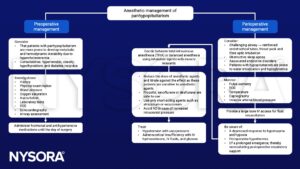
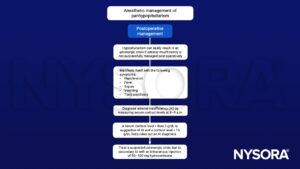
Management
Suggested reading
- Raut MS, Kar S, Maheshwari A, Shivnani G, Dubey S. Perioperative management in a patient with panhypopituitarism – evidence based approach: a case report. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2019;3(3):ytz145. Published 2019 Sep 18.
- Malhotra, Surender & Jangra, Kiran & Saini, Vikas. (2013). Pituitary Surgery and Anesthetic Management: An Update. World Journal of Endocrine Surgery. 5. 1-5. 10.5005/jp-journals-10002-1114.
- Menon R, Murphy PG, Lidnley AM. 2011. Anaesthesia and pituitary disease. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 11;4:133-137.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com