Learning objectives
- Describe the principles, indications, and contraindications of fiberoptic intubation
- Perform fiberoptic intubation
- Describe the possible complications of fiberoptic intubation
Background
- Fiberoptic intubation can be performed in awake (with or without sedation) or anesthetized patients
- Awake fiberoptic intubation is the gold standard for anticipated difficult airways
- Based on the optical characteristics of very thin flexible glass fibers that are capable of transmitting light over their length
- Insulation of these fibers by a glass layer with a different optical density facilitates transmission by the internal reflection of light
- In combination with a light source and lenses on both ends of the fiberoptic bronchoscope, images can be transmitted from the tip of the scope to the eyepiece
Indications & contraindications
- Indications
- Known difficult intubation or previous awake fiberoptic intubation
- Anticipated difficult intubation
- After failed intubation in unanticipated difficult airway
- Known or suspected difficult mask ventilation
- Unstable C-spine
- Abnormal anatomy (congenital airway deformities, head and neck cancers)
- Face/neck/upper airway trauma
- Contraindications
- Absolute
- Patient refusal or inability to cooperate
- Relative
- Lack of trained personnel
- Risk of impending airway obstruction
- Coagulopathy or bleeding in the airway
- Allergy to local anesthetic
- Base of skull fracture (for nasal route)
- Absolute
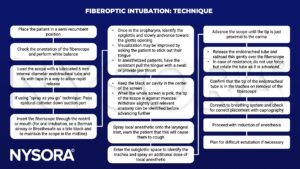
Technique

Complications
-
- Oversedation
- Respiratory depression
- Airway obstruction
- Apnea
- Trauma
- Bleeding
- Laryngospasm
- Vomiting
- Local anesthetic allergy
- Toxicity
- Risk of aspiration due to loss of laryngeal reflexes
Suggested reading
- Pollard BJ, Kitchen, G. Handbook of Clinical Anaesthesia. Fourth Edition. CRC Press. 2018. 978-1-4987-6289-2.
- Collins SR, Blank RS. Fiberoptic intubation: an overview and update. Respir Care. 2014;59(6):865-880.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com