Learning objectives
- Recognize Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
- Management of DIC
Definition and mechanisms
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation is a life-threatening disease characterized by systemic activation of blood coagulation
- Resulting in the generation and deposition of fibrin
- Leading to microvascular thrombi in various organs and contributing to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)
- Consumption of clotting factors and platelets in DIC can result in life-threatening hemorrhage
- Hence, a patient with DIC can present with a simultaneously occurring thrombotic and bleeding problem, obviously complicating the proper treatment
- DIC affects about 10% of very ill patients with sepsis, cancer, or pancreatitis or patients recovering from traumatic injuries such as burns or serious complications from pregnancy and delivery
Signs and symptoms
- Bleeding at wound sites or from the nose, gums, or mouth
- Blood in the stool or urine
- Bruising
- Chest pain
- Pain, redness, warmth, and swelling of the leg
- Confusion, memory loss, or change of behavior
- Difficulty breathing
- Fever
Causes
| Sepsis | |
| Major damage to organs or tissues | Cirrhosis Pancreatitis Severe injury Burns Major surgery |
| Severe immune reactions | Failed blood transfusion Organ transplant rejection Toxin: snake venom |
| Serious pregnancy-related problems | Separation of the placenta from the uterus before delivery Amniotic fluid in the bloodstream Serious bleeding during or after delivery |
| Cancer | |
| Covid-19 |
Complications
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract
- Heart attack
- Shock
- Stroke
- Venous thromboembolism
Diagnosis
| International Society of Thrombosis and Hemostatis criteria | |
|---|---|
| Clinical condition predisposing to DIC | Essential |
| The presence of clinical symptoms | Not used |
| Platelet count (in x 109/L) | 50-100: 1 point -50: 2 points |
| Fibrin-related marker | Moderate increase: 2 points Marked increase: 3 points |
| Fibrinogen | <1: 1 point |
| Prohtrombin time | > 6: 2 points |
| DIC diagnosis | ≥ 5 points |
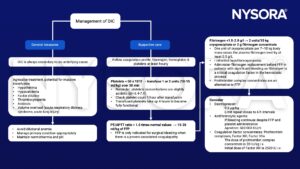
Management
Suggested reading
- Thachil J. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: A Practical Approach. Anesthesiology. 2016;125(1):230-236.
- Ridley, S., Taylor, B., Gunning, K., 2007. Medical management of bleeding in critically ill patients. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain 7, 116–121.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com