Learning objectives
- Defining, diagnosing, and managing hyponatremia
Definition
- Hyponatremia is defined as:
- Mild: a serum sodium concentration between 130-135 mmol/l
- Moderate: a serum sodium concentration between 125-129 mmol/l
- Severe at a serum sodium concentration <125 mmol/l
- Hyponatremia is acute if it is documented to exist <48 hours and chronic if it is documented to exist for at least 48 hours
- If unsure, consider chronic hyponatremia unless there is clinical or anamnestic evidence of the contrary
Signs and symptoms
- Moderate symptoms
- Nausea without vomiting
- Confusion
- Headache
- Severe symptoms
- Vomiting
- Cardiorespiratory distress
- Somnolence
- Seizures
- Coma
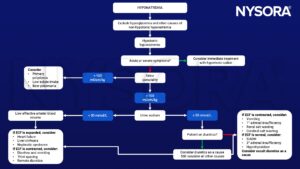
Differential diagnosis
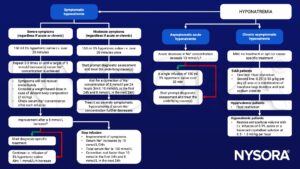
Management
Suggested reading
- Spasovski G, Vanholder R, Allolio B, et al. Clinical practice guideline on diagnosis and treatment of hyponatraemia [published correction appears in Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014 Jun;40(6):924]. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29 Suppl 2:i1-i39.
- Hoorn EJ, Zietse R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyponatremia: Compilation of the Guidelines. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(5):1340-1349.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com