Definition and additional facts
- Drowning is a type of suffocation induced by the submersion of the mouth and nose in a liquid
- The third leading cause of unintentional death
- 360,000 drowning victims annually worldwide
- Submersion time is the strongest predictor of outcome
- Patients require a trauma/ATLS approach
- Problem: survival after cardiac arrest from drowning-related asphyxia is rare
- 100% mortality = submersion > 25 min, resuscitation > 25 min, pulseless on arrival to ER, unconscious at the scene and on arrival to ED
- Most survivors sustain severe CNS injury
Mechanisms of injury
- Hypoxia due to inhalation of fluid in the lungs, potentially leading to cardiac arrest
- Hypothermia:
- Coagulopathy
- Arrhythmias
- Hypovolemia
- Rewarming technique
- Electrolyte abnormalities
- Coagulopathy:
- Arrhythmias
- Hypovolemia
- Rewarming technique
- Electrolyte abnormalities
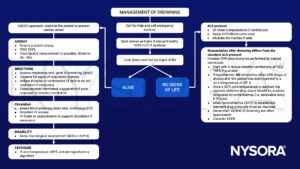
Management
Suggested reading
- Lott C, Truhlář A, Alfonzo A, et al. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021: Cardiac arrest in special circumstances. Resuscitation. 2021;161:152-219.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com