Learning objectives
- Define and recognize aortic stenosis
- Describe the pathophysiology of aortic stenosis and its consequences
- Describe the general anesthetic management principles for aortic stenosis
Definition & mechanisms
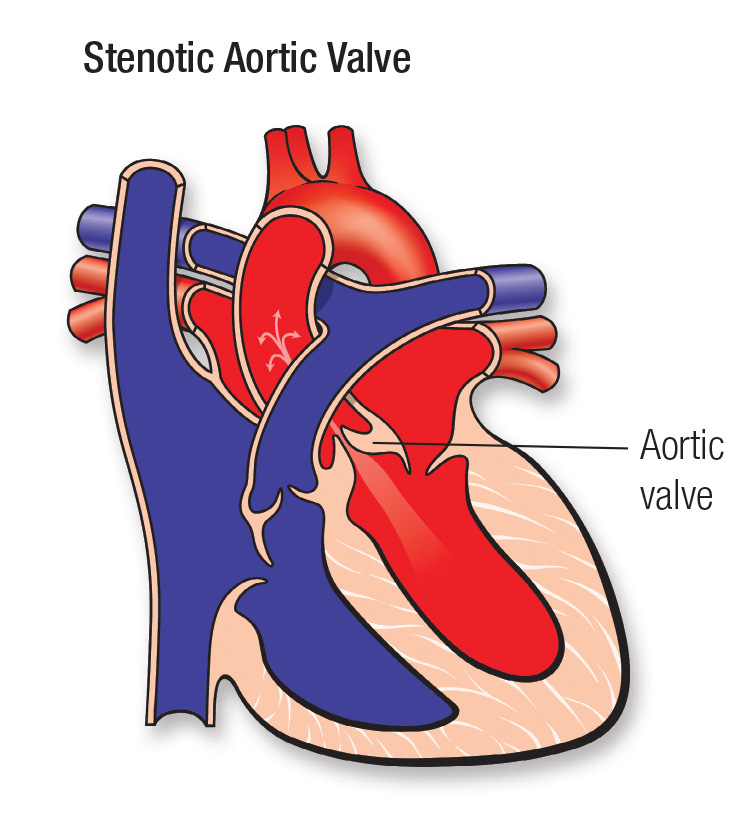
- Aortic stenosis occurs when the aortic valve narrows and blood cannot flow normally
- Severe aortic stenosis is a risk factor for perioperative cardiac complications in non-cardiac surgery
- There are several causal mechanisms:
- Degenerative calcific aortic stenosis: Progressive fibrosis and calcification due to mechanical stress over time
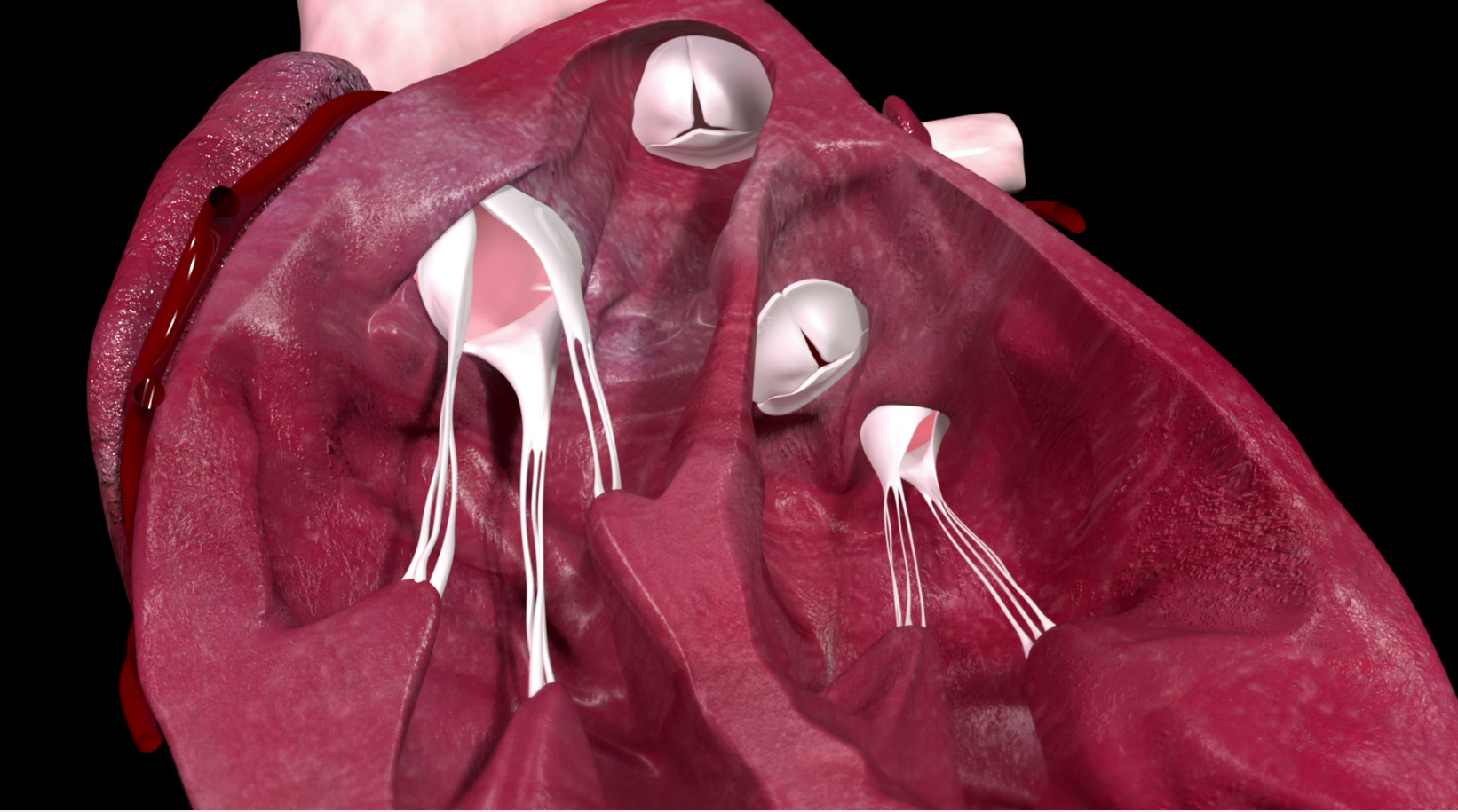
- Congenital bicuspid aortic valve: Abnormal valve structure, with two rather than three leaflets, which can produce fibrosis and calcifications
- Rheumatic aortic stenosis: Long-term consequence of acute rheumatic fever
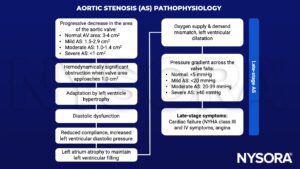
Severity assessment
| Aortic sclerosis | Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak velocity (m/s) | <_2.5 m/s | 2.6–2.9 | 3.0–4.0 | ≥4.0 |
| Mean gradient (mmHg) | - | <20 | 20–40 | ≥40 |
| AVA (cm2) | - | >1.5 | 1.0–1.5 | <1.0 |
| Indexed AVA (cm2 /m2) | - | >0.85 | 0.60–0.85 | <0.6 |
| Velocity ratio | - | >0.50 | 0.25–0.50 | <0.25 |
Anesthetic management
- The severity and pathophysiology of aortic stenosis determine the anesthetic management plan
- The following general principles apply:

Keep in mind
- All necessary medications and equipment to ensure stable vital signals and treat irregularities must be available during the procedure
Suggested reading
- Schneider AC. A review of aortic stenosis: an anesthetic perspective. J Anesth Crit Care Open Access. 2018;10(6):262‒264.
- Baumgartner H Chair, Hung J Co-Chair, Bermejo J, et al. Recommendations on the echocardiographic assessment of aortic valve stenosis: a focused update from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging and the American Society of Echocardiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;18(3):254-275.
- Brown J, Morgan-Hughes NJ. Aortic stenosis and non-cardiac surgery. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 2005;5(1):1-4.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us at [email protected]