Learning objectives
- Definition of polymyositis and dermatomyositis
- Management of polymyositis and dermatomyositis
Definition and mechanisms
- Myositis is the name for a group of rare conditions such as polymyositis and dermatomyositis, leading to weak, painful, or aching muscles
- Polymyositis and dermatomyositis are autoimmune myopathies characterized by inflammation and weakness of proximal skeletal muscles
- Characteristically there is a rise in serum enzymes derived from muscle, e.g. creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and myoglobin may be released leading to myoglobinuria
- Dermatomyositis, unlike polymyositis, is associated with a variety of characteristic skin manifestations
- The cause is unknown, maybe an immune reaction triggered by a virus or tumor
- Both occur almost two times more often in women than in men
- It can occur at any age
Signs and symptoms
- Both polymyositis and dermatomyositis have symptoms in common with sclerosis or sometimes systemic lupus erythematosus:
- Muscle weakness
- Contraction of the arms and legs
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty swallowing
- Muscle tenderness or pain
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Fever
- Feeling tired
- Weight loss
- If dermatomyositis occurs along with polymyositis, symptoms may also include:
- Skin rash
- Swelling around the eye
- Swelling at the base and sides of the fingernails
- Splitting of the skin of the fingers
Diagnosis
- Laboratory findings:
- Elevations in serum creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, aldolase, and aminotransferases
- Myositis-specific autoantibodies
- Muscle biopsy
- Electromyogram
- MRI
Treatment
- Corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressive drugs: methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil, azathioprine, cyclosporine
- Immunoglobulin therapy
- Exercise is important to reduce swelling and to build or restore muscle strength
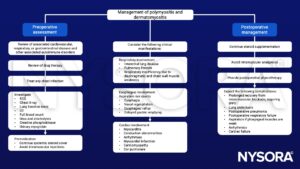
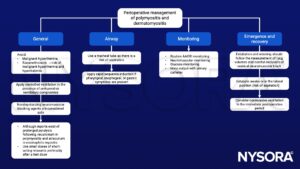
Management
Suggested reading
- Christopher-Stine L, Vleugels An Amato AA. 2022 Clinical manifestations of dermatomyositis and polymyositis in adults. Up To Date.
- Pollard BJ, Kitchen, G. Handbook of Clinical Anaesthesia. Fourth Edition. CRC Press. 2018. 978-1-4987-6289-2.
- Raychaudhuri SP, Mitra A. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis: Disease spectrum and classification. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57(5):366-370.
- Dalakas MC, Hohlfeld R. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet. 2003;362(9388):971-982.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com