Learning objectives
- Complications and anesthetic management of carotid endarterectomy
Definition and mechanisms
- A surgical procedure to remove a build-up of fatty deposits (plaque), which cause narrowing of a carotid artery
- The carotid arteries are the main blood vessels that supply blood to the neck, face, and brain
- The carotid artery may become blocked or a clot is formed leading to a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Carotid endarterectomy significantly reduces the risk of a stroke or TIA
Complications
- Stroke or TIA
- Myocardial infarction
- Cranial nerve injury
- Pooling of blood into the tissue around the incision site causes swelling
- Intracerebral hemorrhage
- Seizures
- Repeated blockage or new blockade of the carotid artery
- Bleeding at the incision site in the neck
- Infection
- High blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeat
- Blocked airway from swelling or from bleeding in the neck
CEA operation
- After careful surgical exposure, the external, internal, and common carotid arteries are cross-clamped
- The carotid bifurcation is isolated from the circulation
- The artery is opened and the plaque will be removed
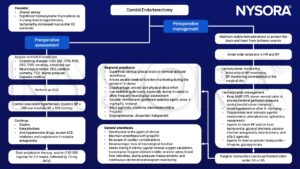
Management
Suggested reading
- Zdrehuş C. Anaesthesia for carotid endarterectomy – general or loco-regional?. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2015;22(1):17-24.
- Howell SJ. Carotid endarterectomy, BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia, Volume 99, Issue 1, July 2007, Pages 119–131.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com