Learning objectives
- Diagnose an inhaled foreign body
- Manage patients with an inhaled foreign body
Background
- Inhaled foreign bodies are a common emergency in young children
- Due to the high position of the larynx and epiglottis and narrow airways, there is a high risk of foreign body aspiration in this age group
- Loss of concentration during physical activity, while eating, or when exploring plastic or metallic objects by putting them in their mouth can result in sudden symptoms of breathing difficulties
- Fourth leading cause of death in young children
- More often in boys compared to girls
Signs & diagnosis
- Signs depend on the type of foreign body, time after aspiration, and exact location of the object, and can range from asymptomatic to severe respiratory distress
- Patients usually present with coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, and rarely with stridor, choking signs, and cyanosis
- The more proximal, the more severe the symptoms
- Many aspirated objects are not radiopaque, resulting in normal-appearing chest radiographs
- Pulmonary infectious or inflammatory infiltration, mediastinal shift, obstructive emphysema, atelectasis, air trapping, and very rarely pneumothorax or pneumomediastinum may be observed
- Normal X-ray results are usually associated with upper airway obstruction, emphysema and infiltration are seen more in distal airway obstruction
- Some organic materials may swell due to fluid absorption, resulting in increased airway blockage
- Sharp objects may perforate the airways
- Eliminate other diagnoses
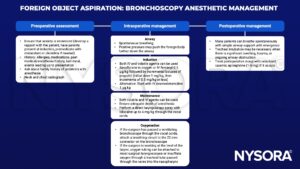
Management
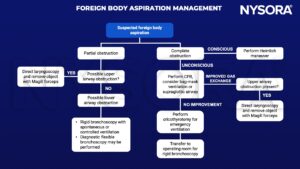
Rigid bronchoscopy anesthetic management
Suggested reading
- Rose D, Dubensky L. Airway Foreign Bodies. [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539756/
- Bould MD. Essential notes: the anaesthetic management of an inhaled foreign body in a child. BJA Education. 2019;19(3):66-7.
- Kendigelen P. The anaesthetic consideration of tracheobronchial foreign body aspiration in children. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8(12):3803-3807.
- Moehrle NP, Jagannathan N. Management of foreign body aspiration in pediatric and adult patients. In: Berkow LC, Sakles JC, eds. Cases in Emergency Airway Management. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2015:79-88.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com