Learning objectives
- Signs and symptoms and management of neurofibromatosis
Definition and mechanisms
- Neurofibromatoses are a group of genetic disorders that cause tumors to form on nerve tissue
- Tumors can develop in the brain, spinal cord, or nerves
- An autosomal dominant disorder caused by a genetic mutation in oncogenes
- Three types of neurofibromatosis:
- Neurofibromatosis 1: usually diagnosed in childhood
- Neurofibromatosis 2: usually diagnosed in early adulthood
- Schwannomatosis: usually diagnosed in early adulthood
- Tumors are usually benign but can sometimes become malignant
Signs and symptoms
| Neurofibromatosis 1 | Neurofibromatosis 2 | Schwannomatosis |
|---|---|---|
| Flat, light brown spots on the skin (cafe au lait spots) Freckling in the armpits or groin area Tiny bumps on the iris of the eye (Lisch nodules) Soft, pea-sized bumps on or under the skin (neurofibromas) Bone deformities Tumor on the optic nerve (optic glioma) Learning disabilities Large than average head size Short stature | Signs and symptoms of NF2 usually result from the development of benign, slow-growing acoustic neuromas Gradual hearing loss Ringing in the ears Poor balance Headaches | Causes tumors to develop on the cranial, spinal, and peripheral nerves Chronic pain, which can occur anywhere in the body and can be disabling Numbness or weakness in various parts of the body Loss of muscle |
| Sometimes NF2 can lead to the growth of schwannomas in other nerves, including the cranial, spinal, visual (optic), and peripheral nerves Numbness and weakness in the arms or legs Pain Balance difficulties Facial drop Vision problems or cataracts Seizures Headache |
Treatment
- Surgical removal
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
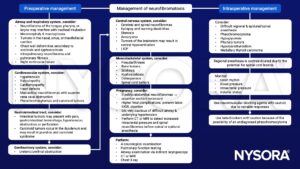
Management
Suggested reading
- Fox CJ, Tomajian S, Kaye AJ, Russo S, Abadie JV, Kaye AD. Perioperative management of neurofibromatosis type 1. Ochsner J. 2012;12(2):111-121.
- Griffiths, S., Durbridge, J.A., 2011. Anaesthetic implications of neurological disease in pregnancy. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain 11, 157–161.
- Hirsch NP, Murphy A, Radcliffe JJ. Neurofibromatosis: clinical presentations and anaesthetic implications. Br J Anaesth. 2001;86(4):555-564.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com