Learning objectives
- Describe the overall mechanisms of cardiac tamponade
- Recognize sings and symptoms of cardiac tamponade
- Diagnose cardiac tamponade
- Anesthetic management of patients with cardiac tamponade
Definition & mechanisms
- Cardiac tamponade is characterized by compression of the heart chambers caused by an accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space
- Common causes:
- Pericarditis
- Tuberculosis
- Trauma
- Malignancy
- Iatrogenic, e.g., after cardiac surgery and invasive procedures
- Intrapericardial pressure increases, causing an increase in right (RV) and left ventricular (LV) filling pressures
- Increased intrapericardial pressure eventually compresses all the cardiac chambers causing a decrease in cardiac output
- Tamponade leads to an exaggerated shift of the interventricular septum to the left during inspiration resulting in impairment of LV filling
- Decrease in systemic arterial pressure of >10 mmHg during inspiration (pulsus paradoxus)
- Crucial factors in the development of tamponade:
- Rate of fluid accumulation relative to pericardial stretch
- Presence or absence of compensatory mechanisms
- Gradually developing effusions are largely asymptomatic, rapidly accumulating effusions can present with tamponade
Signs & symptoms
- Symptoms:
- Dyspnea (usually the first and most sensitive)
- Orthopnea
- Chest discomfort
- Clinical manifestations are consistent with low cardiac output and high central venous pressure:
- Low mean arterial pressure
- Cool peripheries
- Signs of poor end-organ perfusion (e.g., low urine output)
- Palpating the pulse reveals an apparent variation in pulse volume due to pulsus paradoxus
- Jugular venous pressure is typically increased, with distended neck veins apparent
- Sympathetic tone is increased and manifests as tachycardia, diaphoresis, anxiety and poor distal perfusion
- A pericardial rub might be heard on auscultation in patients with inflammatory pericardial disease
Diagnosis
- Chest X-ray: Enlarged globular cardiac silhouette in chronic large pericardial effusions
- ECG:
- QRS complexes may be lower
- Sinus tachycardia is common
- Atrial dysrhythmias may be present
- Beat-to-beat variation in both amplitude and axis of the QRS complexes may be present in patients with large effusions
- Transthoracic (TTE) or transesophageal echocardiography (TEE): determine the size, location, and hemodynamic effects of the pericardial effusion:
- Effusions up to 10 mm in thickness during diastole are considered small, between 10 and 20 mm moderate, and greater than 20 mm large
- Collapse of the cardiac chambers
- Inferior vena cava dilatation
- Increased respiratory variation in the intracardiac blood flow measured with Doppler
- Excessive leftward shift of the interventricular septum during spontaneous inspiration
- Differential diagnoses:
- Epicardial fat
- Pleural effusions
Management
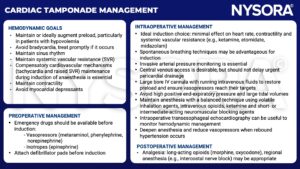
Keep in mind
- Cardiac tamponade is an emergency requiring relief of the pressure effect of the pericardial fluid
- This is achieved by drainage procedures, which can be percutaneous or open surgical techniques
Suggested reading
- Madhivathanan PR, Corredor C, Smith A. Perioperative implications of pericardial effusions and cardiac tamponade. BJA Educ. 2020;20(7):226-234.
- Clinical Anesthesiology: 5th Edition, Morgan, GE, Mikhail, MS, Murray, MJ. Anesthesia for Cardiac Surgery: Cardiac Tamponade. 474-76.
- Essence of Anesthesia Practice: 4th Edition, Fleisher, LA, Roizen, Michael, F, Roizen. Cardiac Tamponade. 76.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us at customerservice@nysora.com