Learning objectives
- Define parathyroidectomy
- Describe the complications that are associated with parathyroidectomy
- Management of a patient undergoing a parathyroidectomy
Definition and classification
- Parathyroidectomy is the surgical removal of one or more of the four parathyroid glands
- The surgery is performed to remove an adenoma or hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands and treat excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH) production (i.e., hyperparathyroidism) and associated hypercalcemia
Indications
- Primary hyperparathyroidism: Hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands (i.e., adenoma, carcinoma, or hyperplasia) leading to an overproduction of PTH
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism: Appropriate compensatory response of the parathyroid glands to secrete more PTH in response to a condition (i.e., chronic kidney disease, vitamin D deficiency) that produces hypocalcemia
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism: Long-standing secondary hyperparathyroidism starts to behave like primary hyperparathyroidism, usually associated with advanced kidney failure
- Ectopic hyperparathyroidism: Secretion of PTH by tissues other than the parathyroid glands
Patient characteristics
- Skeletal muscle weakness, myopathy
- Nephrolithiasis, polyuria, polydipsia, renal failure
- Anemia
- Peptic ulcer disease, vomiting, pancreatitis
- Hypertension, prolonged PR interval, short QT interval
- Generalized osteopenia, bone pain, pathological fractures
- A decline in mental function, personality changes, lethargy, mood disturbances
Complications
- Hypoparathyroidism and associated hypocalcemia
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve damage
- Hematoma
- Infection
- Edema of the glottis and pharynx
Management
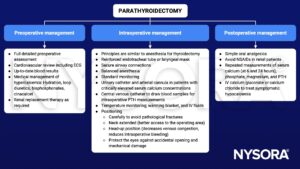
See also thyroidectomy considerations
Suggested reading
- Pollard BJ, Kitchen G. Handbook of Clinical Anaesthesia. 4th ed. Taylor & Francis group; 2018. Chapter 20 Head and neck surgery, Macnab R and Bexon K.
- Malhotra S, Sodhi V. Anaesthesia for thyroid and parathyroid surgery. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 2007;7(2):55-58.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com