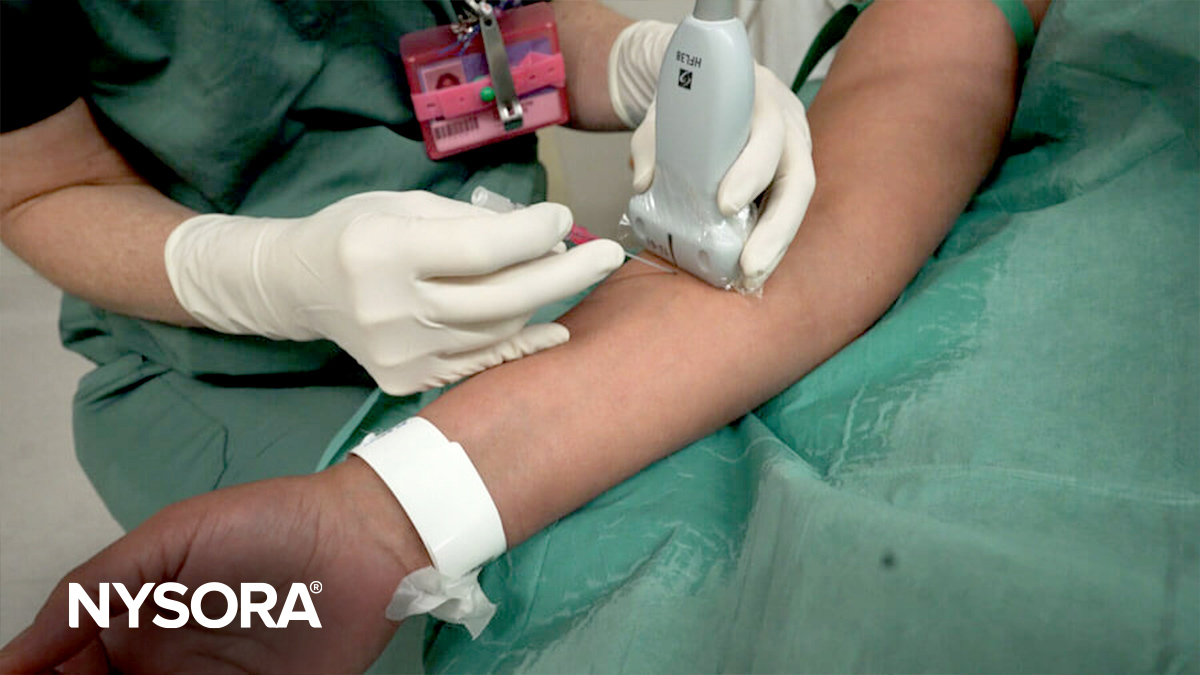
Two views are typically used in ultrasound-guided peripheral venous cannulation: in-plane and out-of-plane. The orientation of the needle with respect to the ultrasound transducer determines whether the needle is in-plane or out-of-plane.
In-plane
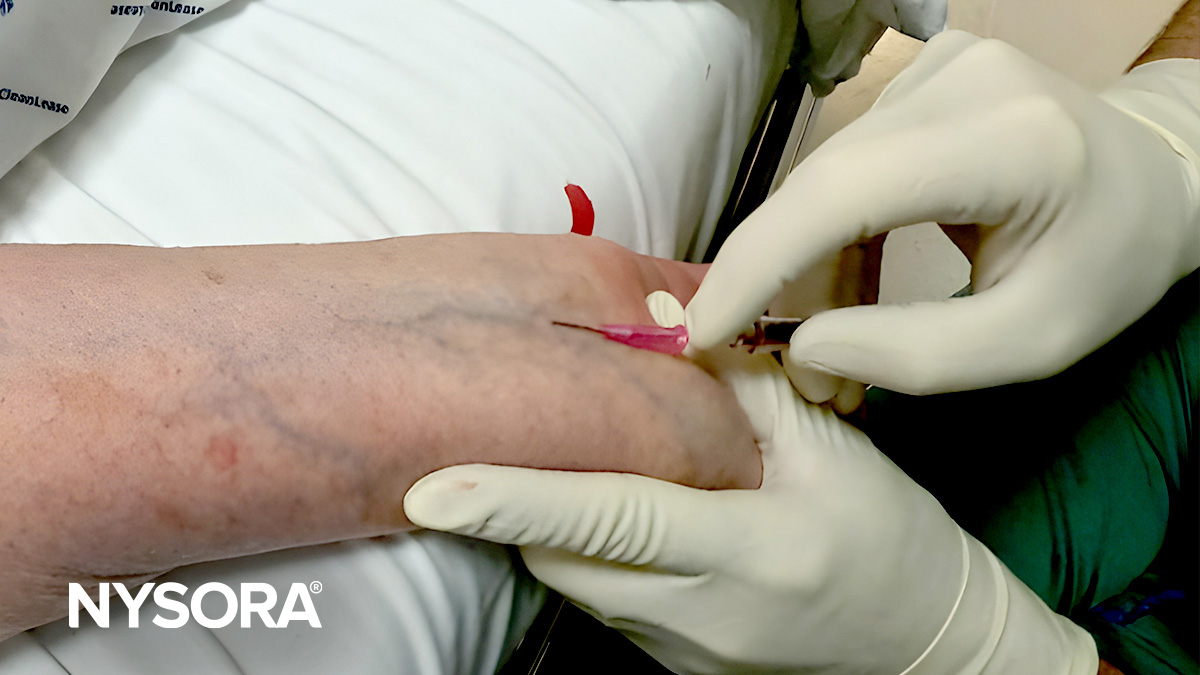
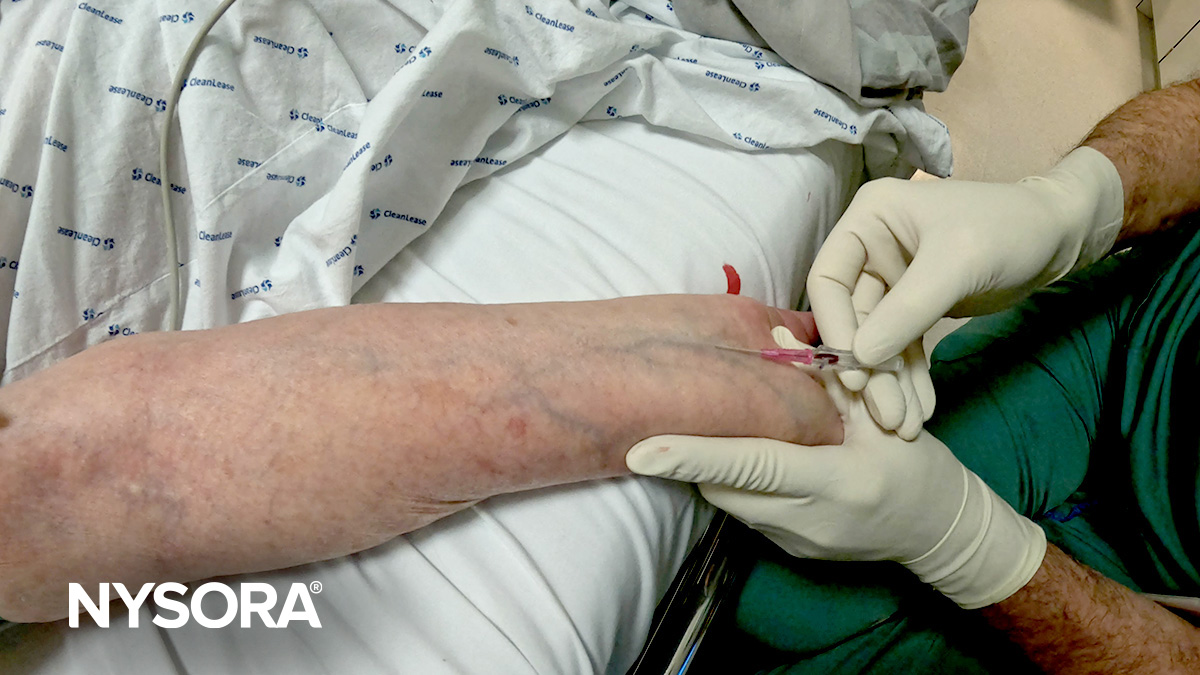
- Description: In-plane is a long-axis approach of the needle. The transducer is aligned with the plane. This view is technically more difficult to obtain as the transducer, vein, and needle all need to be kept in one plane.
- Visualization: The entire needle length and vein trajectory can be seen as a straight line on the ultrasound screen.
- Advantages: The entire shaft of the needle can be visualized, reducing the risk of complications due to incorrect needle advancement. (The angle, direction, and depth can be adjusted.)
- Disadvantages: Requires more space to maneuver as the needle and transducer are aligned in the same plane.
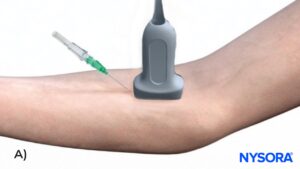
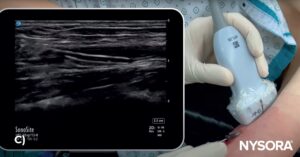
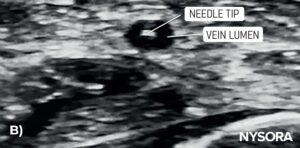
A) Illustration of in-plane needle insertion. B) Ultrasound image of in-plane needle insertion. C) In-plane visualization of the needle using ultrasound guidance.
Out-of-plane
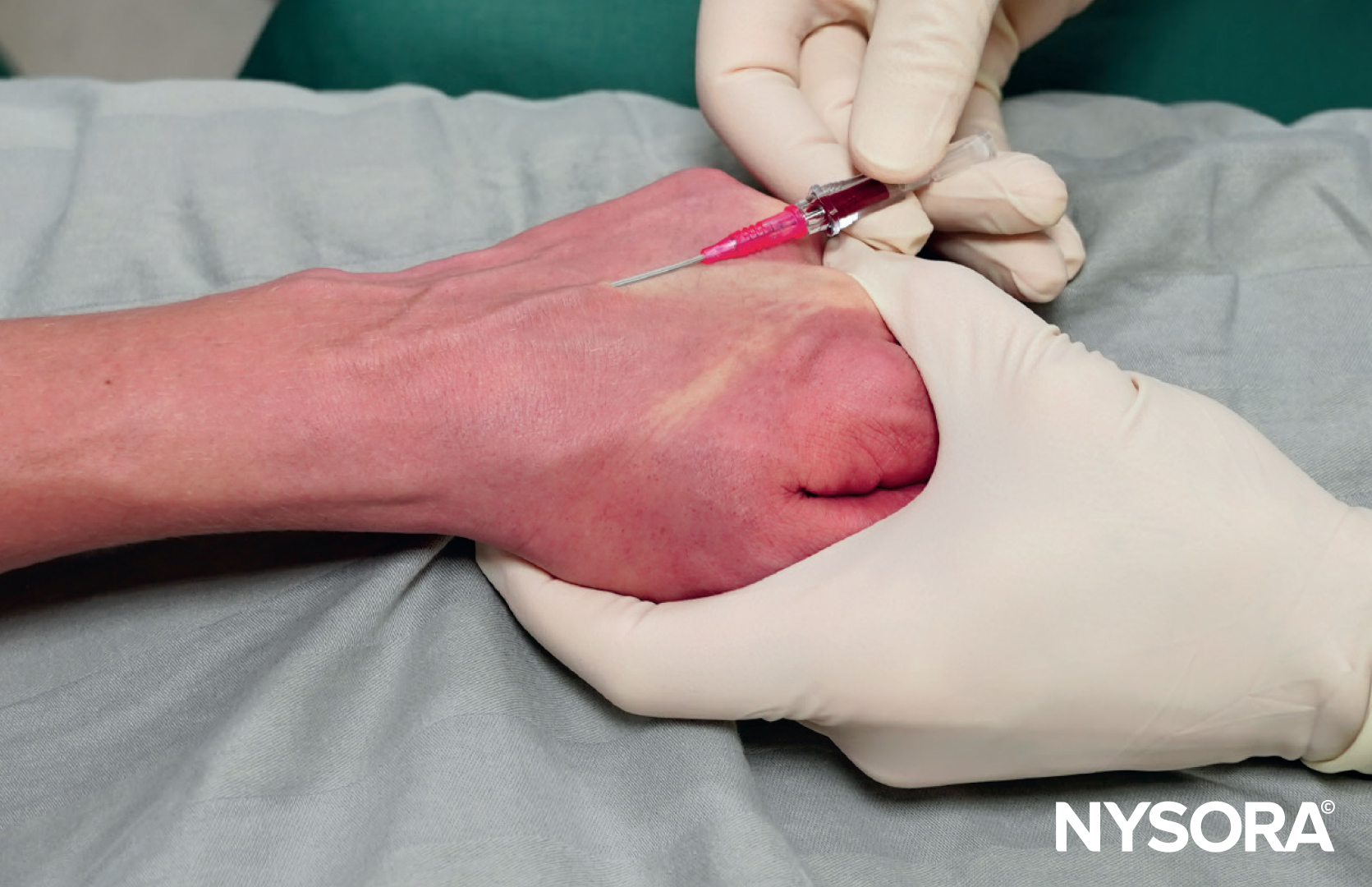
- Description: The out-of-plane technique positions the transducer in a transverse or short-axis orientation with respect to the needle and vessel.
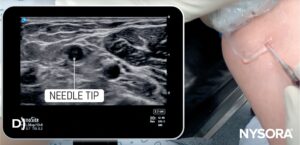
- Visualization: The cross-section of the vessel and a small cross-section of the needle can be seen on the ultrasound screen, typically as a hyperechoic (white) small dot or circle.
- Advantages: This approach requires less space for needle insertion and can be advantageous in anatomically challenging areas.
- Disadvantages: It is harder to determine the exact depth and position as the needle tip can be distinguished only by the appearance and disappearance of the white dot as the imaging plane traverses the needle tip.
- Note: The out-of-plane view is usually preferred for vascular access because it is easy to obtain and is the best for identifying veins and arteries and their orientation relative to each other.
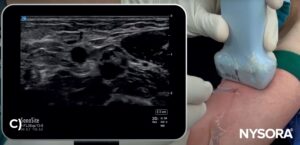
A) Illustration of out-of-plane needle insertion. B) Ultrasound image of out-of-plane needle insertion. C) Out-of-plane visualization of the needle using ultrasound guidance. D) Out-of-plane visualization of the needle tip using ultrasound guidance.
TIPS
- Align the transducer marker with the screen marker for clarity.
- Apply enough gel and place the transducer directly on the skin to get a clear image.
- Do not apply too much pressure on the ultrasound transducer to avoid vein collapse.
- If there is difficulty in visualizing the needle tip, adjust the transducer’s position rather than the needle.