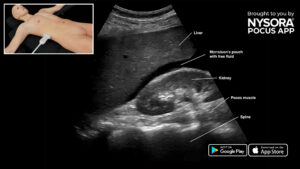
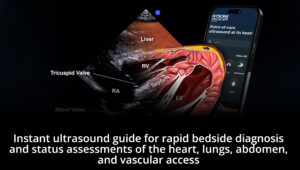
The exam for free intraperitoneal fluid is a “rule-in” exam and is specifically focused on the detection of intra-abdominal fluid.
Abdominal free fluid is often present with:
- Hepatic, renal, or cardiac failure (ascites)
- Inflammation or abdominal sepsis
- Hemorrhage
- Malignancy
Assess this view to detect free fluid in the right thorax and abdomen.
- Position the transducer between the mid- and posterior axillary line at the level of the xiphoid process with the orientation marker toward the head of the patient.
- Scan caudally until you visualize the liver and kidney.
- Structures of interest: Lung, diaphragm, liver, kidney, Morrison’s pouch (virtual space between liver and kidney).
Normal sonoanatomy
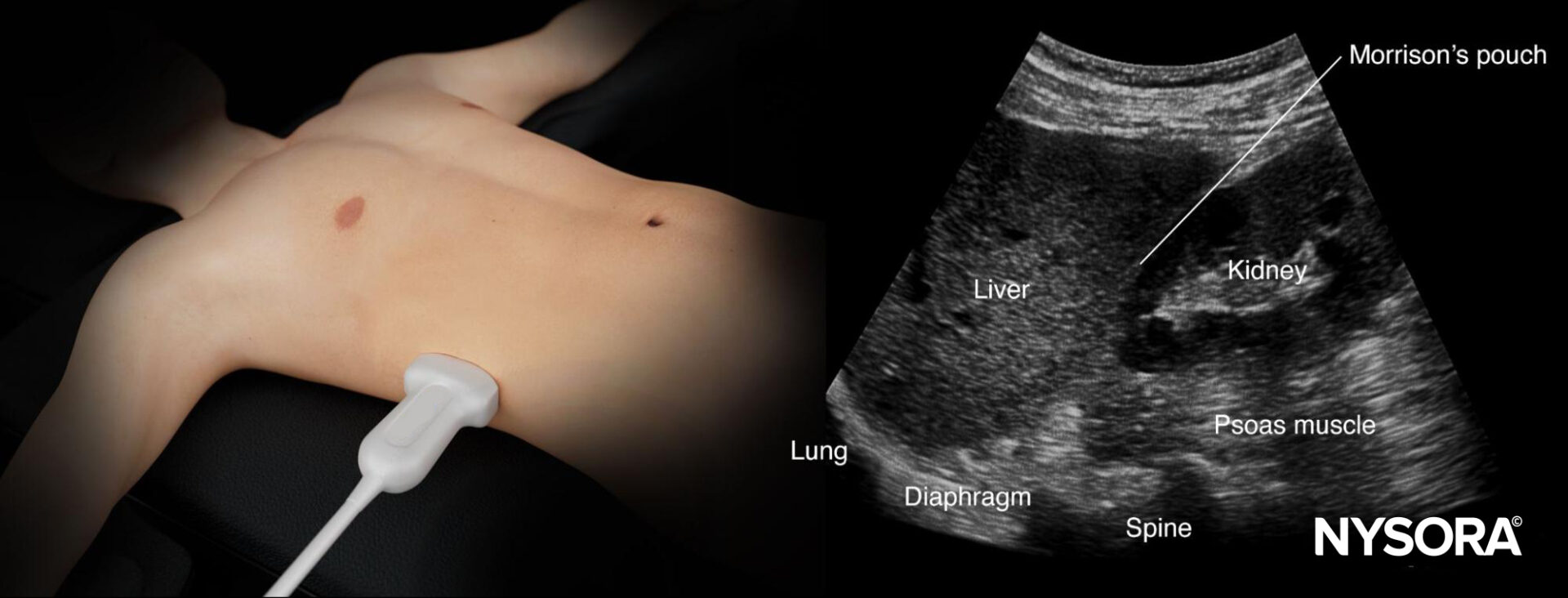
Ultrasound anatomy of the right upper quadrant and relevant anatomical structures
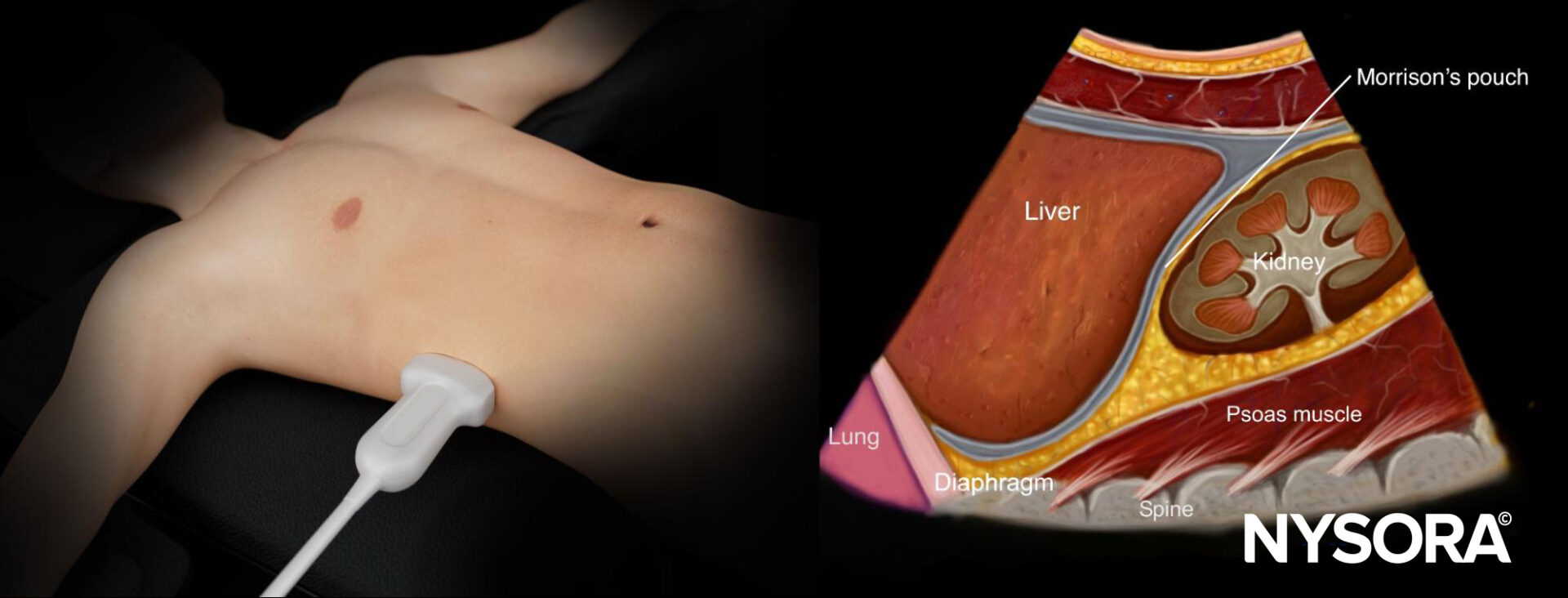
Reverse Ultrasound Anatomy of the right upper quadrant and relevant anatomical structures
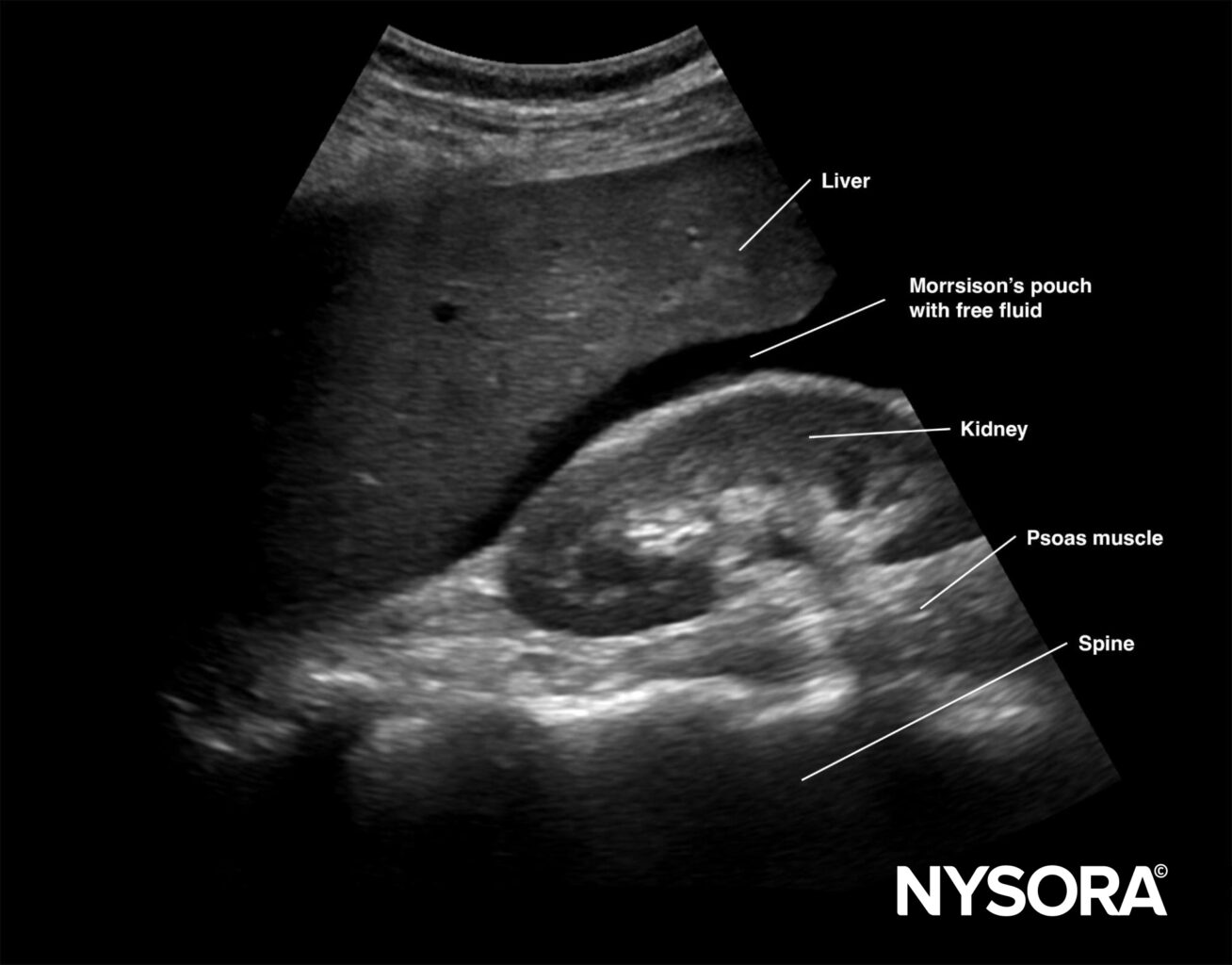
Free intraperitoneal fluid
Free right intraperitoneal fluid collects between the liver and kidney (Morrison’s pouch). If the intrathoracic free fluid is present, it can be identified above the diaphragm.
Unleash the potential of POCUS with NYSORA’s POCUS App and elevate your practice, expand your capabilities, and deliver exceptional patient care. Download HERE.