Learning objectives
- Describe the indications for and types of pneumonectomy
- Manage patients presenting for pneumonectomy
Background
- Pneumonectomy involves the surgical removal of an entire lung
- Should only be considered if all other options, including sleeve lobectomy and non-anatomical resections, have been deemed inappropriate
Indications
- Bronchial carcinoma
- Traumatic injury to the lung with uncontrolled hemorrhage
- Chronic infective disorders of the lung (e.g., tuberculosis)
- Fungal infections resulting in lung destruction
Types of pneumonectomy
- Standard pneumonectomy: Removal of the affected lung only
- Intrapericardial pneumonectomy: Longitudinal opening of the pericardium behind the phrenic nerve, indicated for locally advanced bronchogenic carcinoma
- Extrapleural pneumonectomy: Radical type of resection sometimes used for selected cases of mesothelioma, involves excision of the affected lung, ipsilateral pleura, hemidiaphragm, and hemipericardium, with patch reconstruction
- Completion pneumonectomy: Excision of the residual lung tissue after resection during previous surgery
- Carinal pneumonectomy: Excision of the lung and carina in patients with tumors of the distal trachea or carina
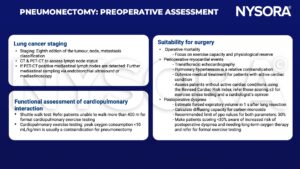
Management


Suggested reading
- Beshara M, Bora V. Pneumonectomy. [Updated 2022 Sep 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555969/
- Hackett S, Jones R, Kapila R. Anaesthesia for pneumonectomy. BJA Educ. 2019;19(9):297-304.
- Lederman D, Easwar J, Feldman J, Shapiro V. Anesthetic considerations for lung resection: preoperative assessment, intraoperative challenges and postoperative analgesia. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(15):356.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com