Learning objectives
- Describe the indications and techniques for thymectomy
- Manage patients presenting for thymectomy
Definition
- Thymectomy is the resection of the thymus gland
- The thymus can enlarge (myasthenia gravis and thymoma) and harbor malignant cells (thymic carcinoma or neuroendocrine tumors)
Indications
- Most common: Myasthenia gravis and thymoma
- Less common: Malignant tumors (thymic carcinoma, neuroendocrine tumors), benign tumors (thymic cysts), ectopic parathyroid glands
Techniques
- Median Sternotomy
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery
- Robotic surgery
Video- and robot-assisted approaches are superior to traditional open approaches
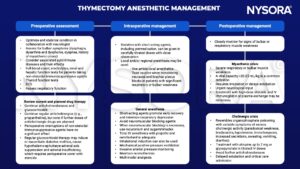
Management
Suggested reading
- Bennett B, Rentea RM. Thymectomy. [Updated 2022 Jul 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564302/
- Daum P, Smelt J, Ibrahim IR. Perioperative management of myasthenia gravis. BJA Education. 2021;21(11):414-9.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com