Learning objectives
- Describe the indications and contraindications for mediastinoscopy
- Describe the possible complications of mediastinoscopy
- Manage patients presenting for mediastinoscopy
Definition
- Mediastinoscopy is a diagnostic procedure with high sensitivity and specificity for lung cancer staging
- Also used for biopsy of mediastinal masses and diagnosis in diseases presenting with mediastinal lymphadenopathy
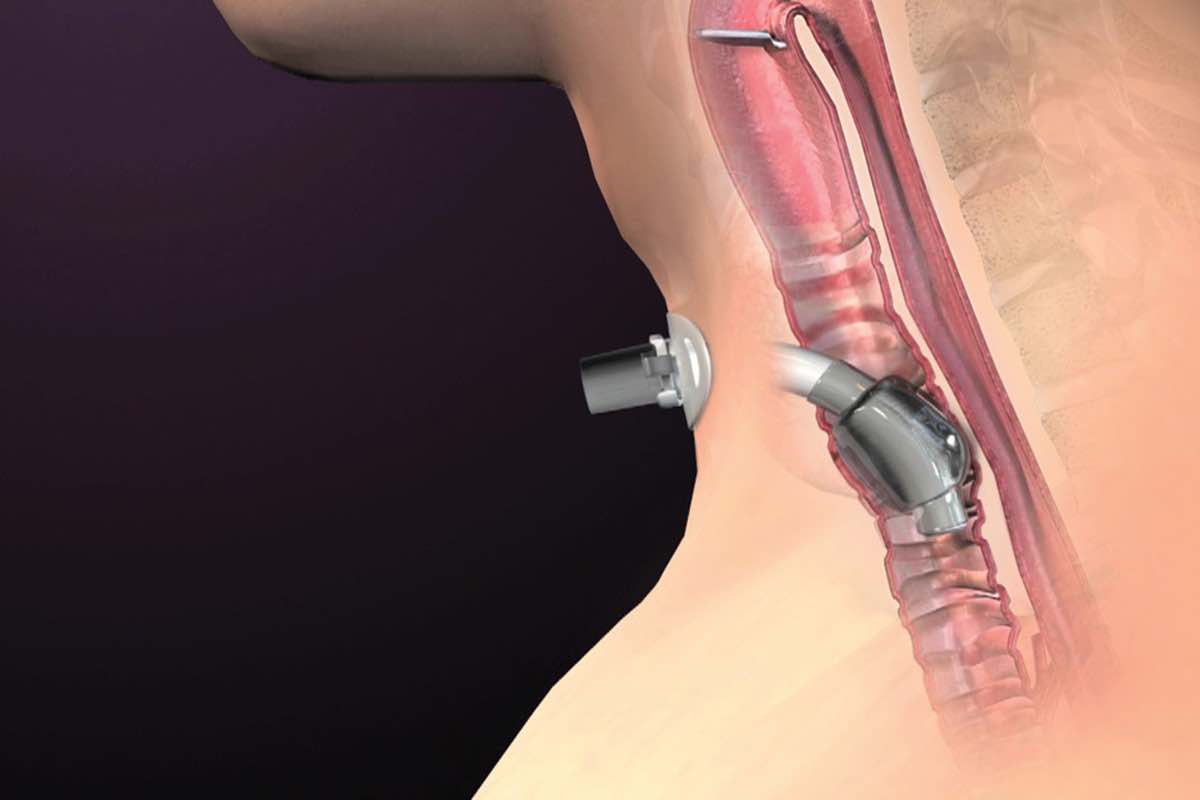
- The majority of mediastinoscopies are performed via the cervical approach:
- Entering the mediastinum through a 3 cm incision in the suprasternal notch
- A dissection is made between the left innominate vein and the sternum creating a tunnel in the fascial layers
- The mediastinoscope is then inserted anterior to the aortic arch
Indication & contraindications
- Indications
- Evaluation of lymph node involvement in patients with carcinoma of the lung
- Tissue biopsy of mediastinal masses
- Removal of mediastinal masses and enlarged lymph nodes
- Conditions presenting as a mediastinal mass:
| Tumors | Anterior mediastinum | Thymic tumors |
| Thyroid and parathyroid tumors | ||
| Lymphoma | ||
| Germ cell tumors | ||
| Middle mediastinum | Lymphoma | |
| Mesenchymal tumors | ||
| Posterior mediastinum | Esophageal cancer | |
| Neurogenic tumors | ||
| Benign conditions | Developmental cysts | Pericardial cyst |
| Esophageal cyst | ||
| Granulomatous lymphadenopathy | Tuberculosis | |
| Sarcoidosis | ||
| Vascular | Aneurysms (e.g., thoracic aorta, innominate vein) | |
| Aberrant vessels (e.g., persistent left superior vena cava, anomalous left pulmonary artery |
- Contraindications
Absolute Anterior mediastinal mass
Inoperable tumor
Previous recurrent laryngeal nerve injury
Extremely debilitated patients
Ascending aortic aneurysm
Previous mediastinoscopy
Relative Thoracic inlet obstruction
SVC syndrome
Severe tracheal deviation
History of radiation therapy to the chest
Cerebrovascular disease
Severe cervical spine disease with limited neck extension
Thoracic aortic aneurysm
Possible complications
- Major hemorrhage
- Stroke
- Air embolism
- Pneumothorax
- Reflex arrhythmias
- Phrenic nerve paralysis
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy
- Esophageal tear
- Tracheobronchial laceration
- Thoracic duct injury
- Minor bleeding
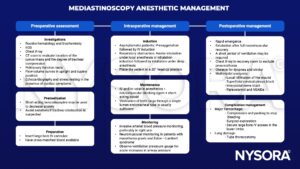
Management
Suggested reading
- McNally PA, Arthur ME. Mediastinoscopy. [Updated 2022 Sep 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534863/
- Ahmed-Nusrath A, Swanevelder J. Anaesthesia for mediastinoscopy. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 2007;7(1):6-9.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com