Learning objectives
- Anesthetic management of laparoscopic surgery
Definition and mechanisms
- A minimally invasive surgical technique to explore the abdominal and pelvic cavities
- 2-4 small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) are made to insert surgical instruments and a laparoscope with a camera at the end
- The laparoscope aids in diagnosis or therapeutic interventions
Risks and benefits of laparoscopic surgery
| Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|
| Reduced wound infection Faster recovery Reduced morbidity Reduced pain | Visceral and vascular damage Complications associated with extremes of positioning Acute kidney injury (AKI) Cardiocerebral vascular insufficiency Pulmonary atelectasis Venous air embolism (VAE) 'Well leg compartment syndrome |
List of surgeries performed laparoscopically
- Cyst, fibroid, stone, and polyp removals
- Small tumor removals
- Biopsies
- Tubal ligation and reversal
- Ectopic pregnancy removal
- Endometriosis surgery
- Urethral and vaginal reconstruction surgery
- Orchiopexy (testicle correction surgery)
- Rectopexy (rectal prolapse repair)
- Hernia repair surgery
- Esophageal anti-reflux surgery (fundoplication)
- Gastric bypass surgery
- Cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) for gallstones
- Appendectomy (appendix removal) for appendicitis
- Colectomy (bowel resection surgery)
- Abdominoperineal resection (rectum removal)
- Cystectomy (bladder removal)
- Prostatectomy (prostate removal)
- Adrenalectomy (adrenal gland removal)
- Nephrectomy (kidney removal)
- Splenectomy (spleen removal)
- Radical nephroureterectomy (for transitional cell cancer)
- Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy) for pancreatic cancer
- Gastrectomy (stomach removal)
- Liver resection
Complications
- Occult hemorrhage – may not be visible due to small surgical field
- Vascular or solid organ injury
- Gas embolism
- Subcutaneous emphysema
- Capnothorax: suspect of unexplained ↑ airway P, hypoxemia, & hypercapnia
- Capnomediastinum & capnopericardium
- Complications related to positioning
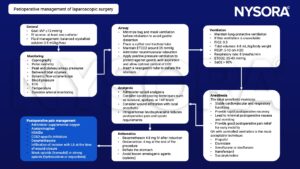
Perioperative management
Suggested reading
- Bajwa SJ, Kulshrestha A. Anaesthesia for laparoscopic surgery: General vs regional anesthesia. J Minim Access Surg. 2016;12(1):4-9.
- Hayden P, Sarah Cowman S. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain, Volume 11, Issue 5, October 2011, Pages 177–180.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us at customerservice@nysora.com