Learning objectives
- Anesthetic management of a patient with Down syndrome
Definition and mechanisms
- Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is a genetic disorder caused by an error in cell division
- Some or all body cells contain 47 chromosomes with the extra chromosome linked to chromosome 21
- Most frequent chromosomal abnormality
Physiological changes
| Physiological changes | |
|---|---|
| Neurological | Mental retardation |
| Airway/Respiratory | Microcephaly Macroglossia Subglottic stenosis Obstructive sleep apnea Airway obstruction Small upper and lower airways Pulmonary hypoplasia Respiratory tract infections |
| Cardiovascular | Complete atrioventricular defect Ventricular septal defect Atrial septal defect (ASD) Conduction disturbances Pulmonary hypertension (PH) |
| Gastrointestinal | Gastroesophageal reflux disease Duodenal atresia Tracheoesophageal fistula Hirschprung disease Imperforate anus |
| Musculoskeletal | Atlantoaxial instability |
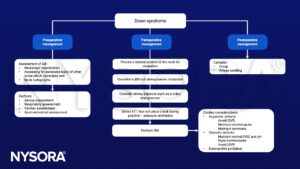
Anesthetic management
Suggested reading
Meitzner MC, Skurnowicz JA. Anesthetic considerations for patients with Down syndrome. AANA J. 2005;73(2):103-107.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com