Explore NYSORA knowledge base for free:

Troubleshooting tips & tricks

Visuals to enhance understanding
Step-by-step tutorials



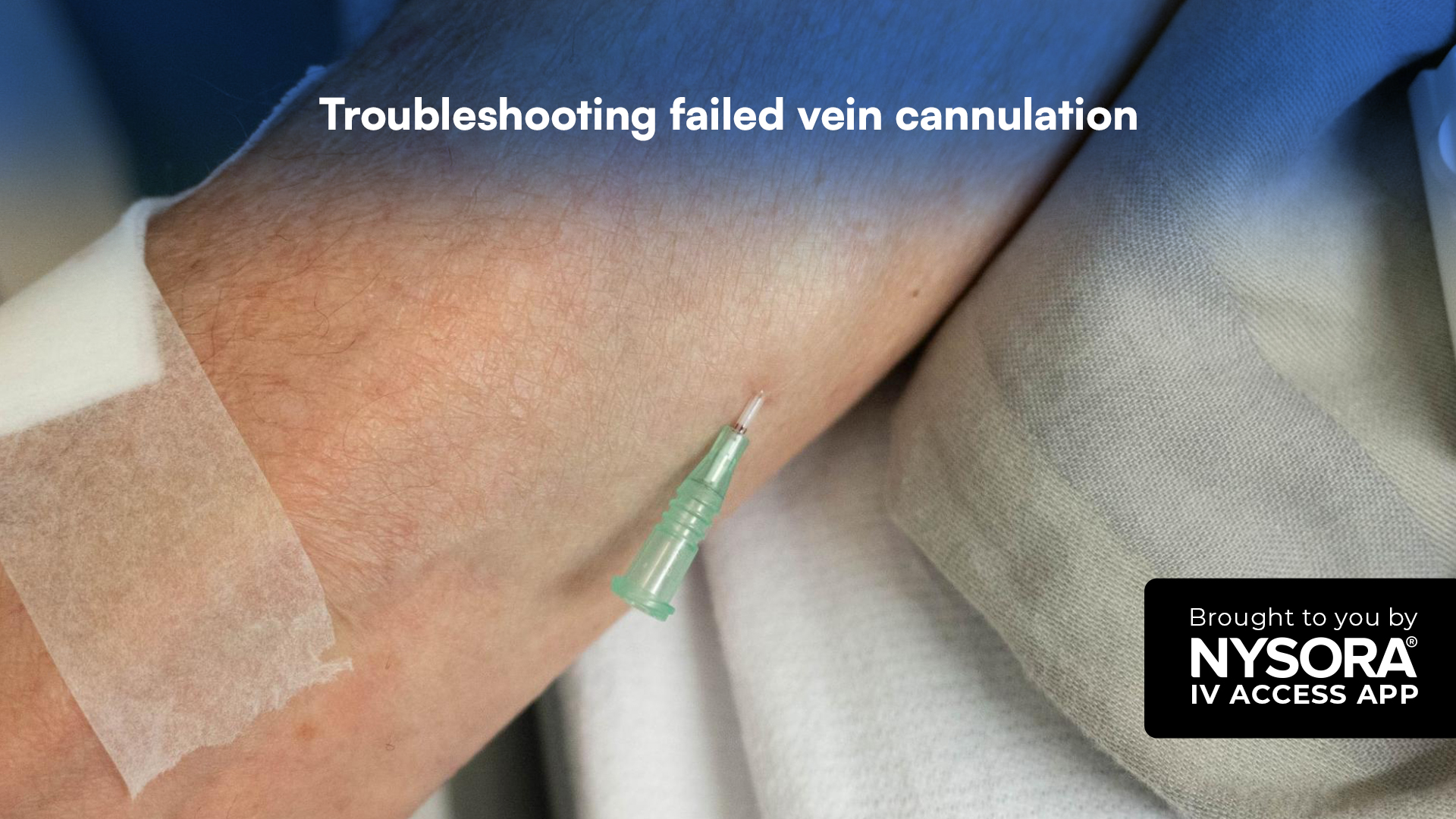
Failed attempts at vein cannulation can be frustrating for both patients and clinicians, increasing patient discomfort and adding stress to medical staff. When a cannulation attempt fails, evaluating the cause and employing specific troubleshooting techniques can significantly improve the success of subsequent attempts. Below, we provide a comprehensive guide on common problems in vein cannulation failure and actionable steps for healthcare providers to take. Understanding common reasons for cannulation failure Failed cannulation can arise from various issues, such as improper needle position, vein occlusion, and patient positioning. Here’s a breakdown of the most common challenges: Incorrect needle position: The needle may be positioned too shallow or misaligned, resulting in the catheter pressing against the vein wall. Vein occlusion: Clotted or thrombosed veins prevent the needle from entering smoothly. Immediate bleeding: Removing a failed catheter can cause bleeding at the insertion site. Tourniquet removal: Releasing the tourniquet prematurely may collapse the vein, complicating future attempts. Strategies for troubleshooting failed cannulation Check needle position Problem: If the needle does not penetrate the vein, it may be positioned either adjacent to or below it. This often results from insufficient depth, with the catheter being pushed against the vein wall rather than entering the vein lumen. Interventions: Increase counter traction: Apply counter traction on the skin to stabilize the vein and improve control during insertion. Adjust needle angle: Modifying the angle can help the needle enter the vein more precisely. Try lowering or raising the needle to achieve better alignment with the vein. Change insertion site or arm position: To improve access, reposition the patient’s arm or choose a different vein. Consider starting with larger, more superficial veins to enhance success rates. Check for vein occlusion Problem: Difficulty inserting the needle could indicate vein occlusion, often signaled by a “rolling” vein that does not permit […]
Intravenous (IV) therapy is a cornerstone of modern medicine, providing essential pathways for administering medications, fluids, and nutrients directly into the bloodstream. Over the years, the use of long-term intravenous devices such as peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC lines), midlines, and implantable ports has expanded significantly, both in hospitals and outpatient settings. These devices, while indispensable, come with their own set of challenges and potential complications. Types of long-term intravenous devices Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) lines: PICC lines are used for medium to long-term infusions, blood transfusions, and frequent blood sampling. They serve as an alternative to implanted ports, especially when short chemotherapy protocols are needed, or when the placement of an implanted port is contraindicated due to conditions like hemostasis disorders or thoracic skin damage. Midlines: These are shorter than PICC lines and have an expected dwell time ranging from 4 weeks to 3 months. Midlines are often used for non-irritant drug administration and parenteral nutrition. Implantable ports: These devices are placed under the skin and provide a reliable option for long-term treatments, such as chemotherapy. They are associated with lower infection rates compared to other types of catheters. Common complications associated with long-term IV devices Thrombotic complications Thrombosis: Catheter-related thrombosis (CRT) is a major complication associated with long-term intravenous devices. Thrombosis can occur at various sites, including the arm or intrathoracic route of the catheter. The risk increases with larger catheter diameters and when the catheter-to-vein ratio exceeds 33-45%. Pulmonary embolism: While less common, PICC line-related deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can lead to pulmonary embolism, a potentially fatal condition. The risk is higher in patients with advanced cancers. Infectious complications Catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs): These infections range from local insertion site infections to bacteremia. Factors that increase infection risk include hematological cancer, parenteral nutrition, and the use of […]

The app includes:
The NYSORA IV Access App provides quick, on-the-go access to expertly-curated techniques, helping you:
The app can be used in multiple ways:
It’s a mobile-friendly reference tool offering: