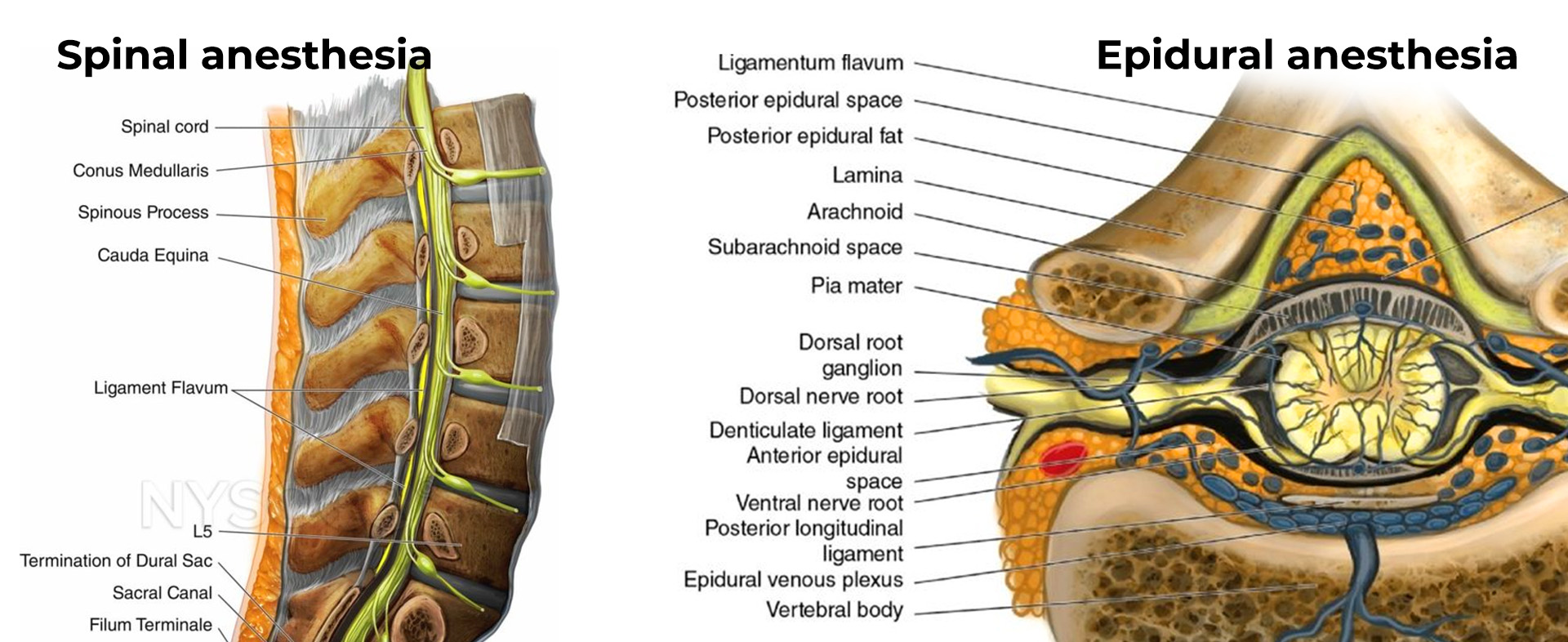
Explore NYSORA knowledge base for free:
Brought to you by NYSORA, a renowned name in anesthesia education.
Navigate through step-by-step technique instructions for over 60 nerve blocks.
Delve into NYSORA’s signature illustrations and videos, including the enlightening Reverse Ultrasound Anatomy, and videos from NYSORA’s clinical practice.
Access cutting-edge content and updates on any device via our desktop platform or handy mobile app.
Most commonly used content for EDRA exam: with specially crafted infographics tailored for exams like EDRA.
Designed for real-world application, get hands-on information tailored for practical use and watch countless, short video tutorials from NYSORA’s clinical practice.