Regional anesthesia using ultrasound guidance is currently a two-person procedure. The anesthesiologist holds and positions the block needle with one hand and holds the ultrasound probe to identify physiology landmarks to confirm needle placement with their other hand. The anesthesiologist then requires an assistant to provide the third hand to operate the syringe to inject the anesthetic.
An innovative new device SAFIRA™, provides an alternative, giving anesthesiologists full control of the injection during regional anesthesia while still being able to hold the needle and the ultrasound probe.
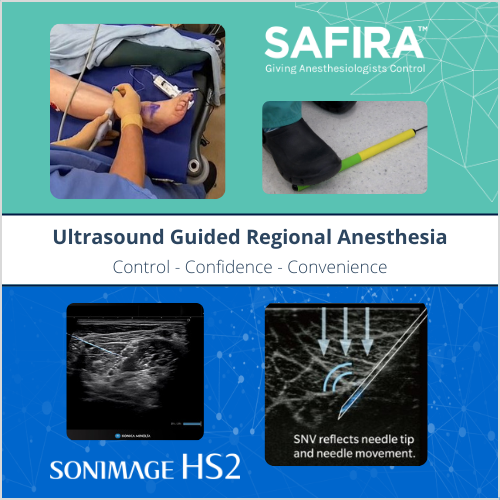
SAFIRA™: SAFer Injection for Regional Anesthesia comprises of a driver, sterile syringe (Luer and NRFit), and foot pedal operator. The anesthesiologist controls aspiration and infusion themselves using the foot pedal operator without the need for an assistant.
Developed with clinicians working in the UK National Health Service (NHS), the device is intuitive to use and incorporate into existing regional anesthesia practice. It also has a built-in safety feature which automatically stops injection at 20-psi, helping to reduce the risk of nerve damage.
Making regional anesthesia a single person procedure enables the anesthesiologist to continue to realise the benefits of using ultrasound guidance, with benefits to the anesthesiologist including being able to confirm the exact placement and spread of the local anesthetic.
Ultrasound has proven to be the imaging modality of choice to guide nerve blocks. The SONIMAGE® HS2 not only provides superior imaging of detailed structures, but also provides needle recognition software. Simple Needle Visualization, SNV®, incorporates an advanced algorithm that utilizes both in-plane and out-of-plane methods to improve needle visibility. Superior visualization is independent of the needle type and independent of the angle at which the needle shaft and ultrasound beam intersect, an advantage for steep angle approaches.
The SNV® feature provides greater needle visibility of the tip, shaft, and injectate for visual confidence at any angle.
As the clinician is in full control of the injection process themselves using SAFIRA™, they are not reliant on the assistant advising of any change in ‘injection feel’ which may require adjustments to be made such as needle position. Prompt action can be taken by the clinician, using the ultrasound image to guide them, and the procedure completed.
The introduction of SAFIRA™ and the SONIMAGE® HS2 System for ultrasound guidance in regional anesthesia will support the refinement of nerve block techniques and encourage expansion of the use of nerve block procedures.
