Michael J. Barrington, Richard Brull, Miguel A. Reina, and Admir Hadzic
INTRODUCTION
This section reviews various factors that may contribute to neurologic complications after peripheral nerve blocks (PNBs) and suggests principles of practice and implications of monitoring modalities to mitigate the risk of neurologic complications.
ANATOMY CONSIDERATIONS OF PERIPHERAL NERVE BLOCK–RELATED NERVE INJURY
A nerve is a distinct organ comprising neural tissue, a specific connective tissue stroma, and a designated blood supply (Figure 1). Nerve cells, or neurons, are composed of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon.
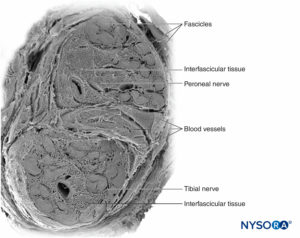
FIGURE 1. Human sciatic nerve. Scanning electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
The axon is a cytoplasmic extension of the neuron that transmits electrical signals along its length from the cell body proximally to anywhere from just a few millimeters up to nearly 1 m distally. Most peripheral nerves can transmit both afferent motor and efferent sensory signals.
In the peripheral nervous system, the vast majority of axons are myelinated, characterized by a sheath of Schwann cells that encase the axon in a layer of myelin (Figure 2). The Schwann cells are interrupted at interposed spaces, known as the nodes of Ranvier, where the process of depolarization and repolarization occurs during the saltatory propagation of the action potential. Together with its myelin sheath, each axon is bound by a thin layer of connective tissue called an endoneurium (Figure 3) and then termed a nerve fiber.
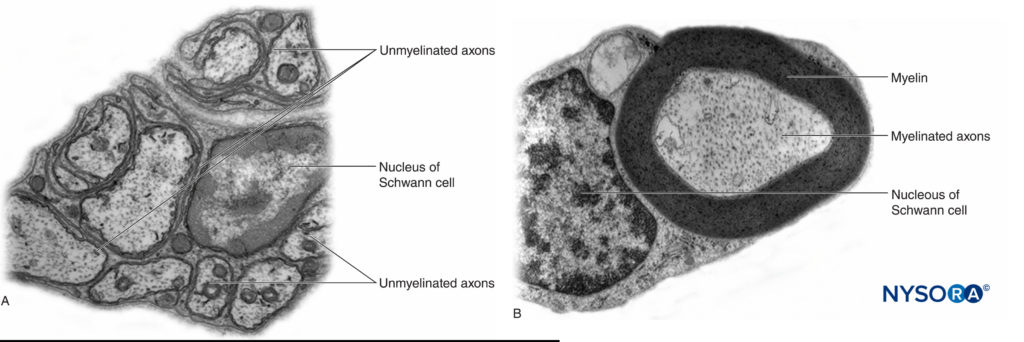
FIGURE 2. A: Unmyelinated axon of a human nerve rootlet. B: Myelinated axon of a human sciatic nerve. Transmission electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
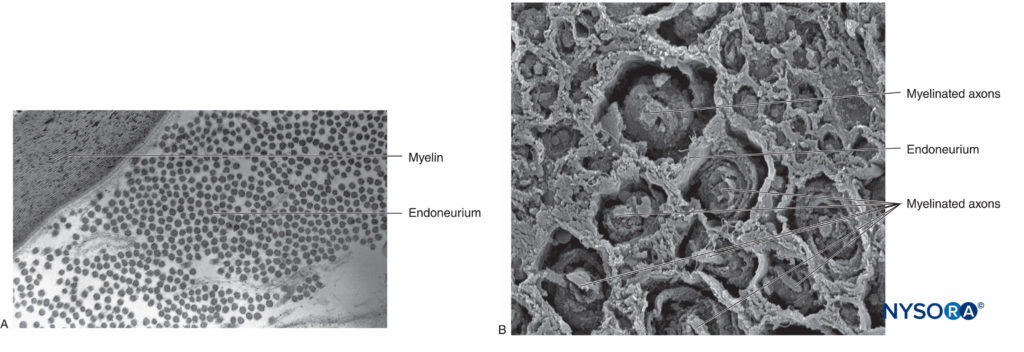
FIGURE 3. Endoneurium. Myelinated axons enveloped by endoneurium obtained from a human sciatic nerve. A: Transmission electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.) B: Scanning electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
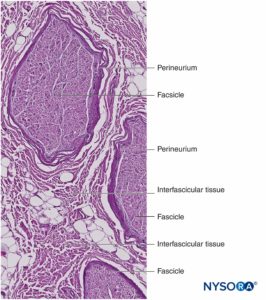
Nerve fibers are organized into groups called fascicles (Figure 4). Within each fascicle, the nerve fibers form an intraneural plexus in which the axons take different positions along their path (Figure 5). In the vicinity of joints, the fascicles are thinner and more numerous and tend to be surrounded by a greater amount of connective tissue, which reduces the vulnerability of the fascicles to insults such as pressure and stretching.
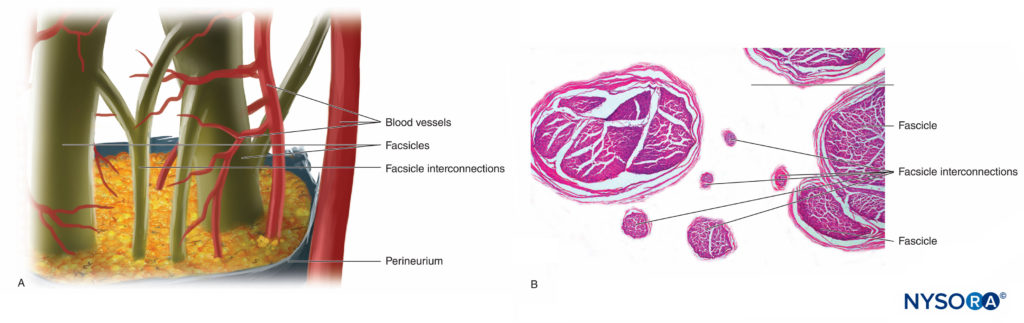
FIGURE 5. Intraneural plexus. A: Diagram. B: Fascicles and interconnection fascicles. (B, Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
Each fascicle is surrounded by perineurium consisting of continuous and concentric layers of 8 to 18 cells (Figure 6). The thickness of the perineurium is typically 7 to 20 μm. The layers of perineurial cells provide a barrier for diffusion of substances into and out of the fascicles. The space between perineurial cells is composed of fundamental amorphous substances, collagen fibers, and fibroblasts. These collagen fibers can be aligned in different directions, but predominantly along the longitudinal axis of the fascicle (Figure 6). The perineurium allows for some movement of axons within a fascicle and maintains intrafascicular pressure while serving as an effective physical barrier against mechanical and chemical injury. Likewise, the perineurium serves as an important diffusion barrier, preventing exposure of the axons to potentially noxious substances, such as local anesthetics.
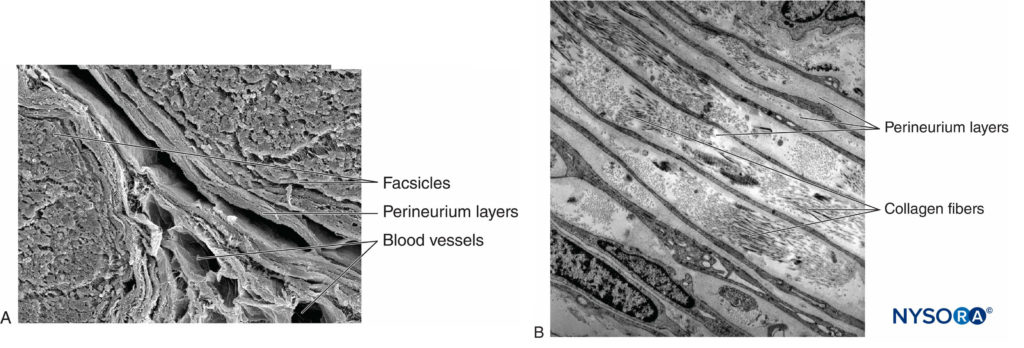
FIGURE 6. Perineurium. Perineural layers of human sciatic nerve. A: Transmission electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA, López A, Villanueva MC, et al: The blood-nerve barrier in peripheral nerves. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2003 Feb;50(2):80-86.) B: Scanning electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
Groups of fascicles are bound together by an epineurium, the thickest of the three connective tissue layers that encase groups of fascicles along with their interfascicular supporting tissue and adipocytes (Figure 1). The epineurium is composed mainly of collagen fibers and a small number of blood vessels (Figure 7). The collagen fibers of the epineurium are similar in size and appearance to collagen fibers of the dura or dural sleeves. The epineurium gives the nerve its characteristic external appearance on ultrasound imaging (ie, it appears as a discrete structure).
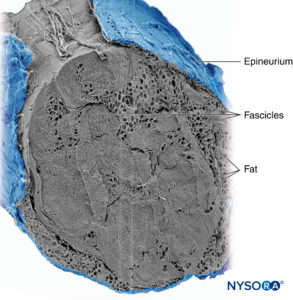
FIGURE 7. Epineurium. Human tibial nerve: detail of fascicles, interfascicular tissue, and epineurium. Scanning electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina
MA, Arriazu R, Collier CB, et al: Electron microscopy of human peripheral nerves of clinical relevance to the practice of nerve
blocks. A structural and ultrastructural review based on original experimental and laboratory data. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2013 Dec;60(10):552–562.)
Peripheral nerves have two independent, yet interconnecting, vascular systems. The extrinsic system consists of arteries, arterioles, and veins that lie within the epineurium, while the intrinsic vascular system comprises a group of longitudinal capillaries that run within the fascicles and endoneurium (Figure 8). Anastomosis between the two vascular systems is formed by vessels (Figure 1) that originate in the epineurium and traverse the perineurium. Injury to these vessels can lead to a range of complications, from ischemia to inflammation due to hematoma.
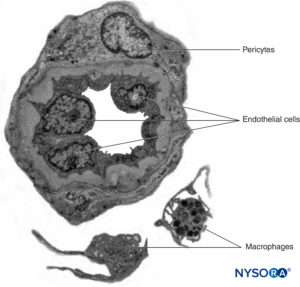
FIGURE 8. Endoneural continuous capillaries. Transmission electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
Nerve roots have less tensile strength and elasticity compared to the axons and their supporting elements in peripheral nerve trunks. Axons included within the spinal nerve roots are not surrounded by a perineurium or other structure with a barrier effect. More distally (eg, spinal nerves and plexus trunks/divisions), fascicles have their own protective perineurium (Figures 9, 10, and 11) and have a plexiform arrangement that contributes to their tensile strength. Nerve trunks within tissue beds, fascicles within nerve trunks, and axons within fascicles have a slight undulating course, resulting in relative excess length. In addition, nerves are often attached loosely by their epineurium to adjacent structures. There is a nonspecialized network of areolar (deep fascial) connective tissue that fills the space between specialized structures such as nerves, muscles, and vessels (Figure 12). This tissue loosely connects these structures so that movement of one on another is permitted. This movement is reduced when nerves are tethered by entering blood vessels, branches, or other landmarks.
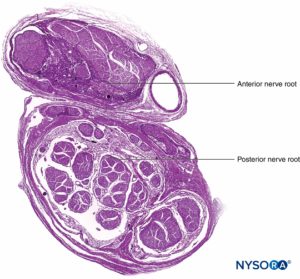
FIGURE 9. Ventral and dorsal nerve root. Transversal section at seventh nerve root cuff between dural sac and dorsal root ganglion. (Used with permission from M.A. Reina.)
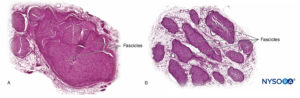
FIGURE 10. Nerve root. Transversal section at seventh nerve root cuff outer dorsal root ganglion. A: Outer to 2 mm. B: Outer to 5 mm. (Used with permission from M.A. Reina.)
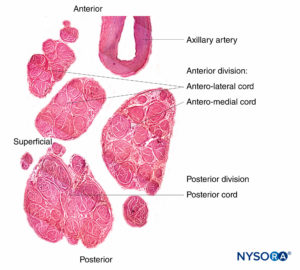
FIGURE 11. Brachial plexus cords. Anteromedial cord, anterolateral cord, and posterior cord. Details of fascicles and interfascicular tissue within the cords. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
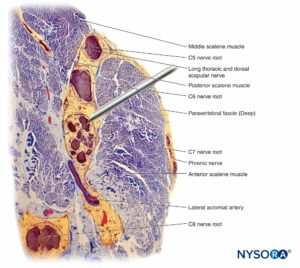
FIGURE 12. Interaction of the block needle and the interscalene brachial plexus. Placement of the needle into fascicles (as shown here) results in fascicular injury. Additional injury can be committed when an injection is being made through an intrafascicularly placed needle. Observe the difference in size between the needle and fascicles. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
For a more comprehensive review, see Connective Tissues of Peripheral Nerves.
NYSORA Tips
Loss of muscle tone, as occurs during anesthesia, theoretically exposes the neural elements to traction forces. However, there are also anatomical features protecting against lateral traction or stretch injury. For example, in the setting of interscalene brachial plexus blocks, the fourth, fifth, and sixth spinal nerve roots are lodged into the gutter of the transverse processes and are therefore relatively protected from these forces. The dorsal and ventral roots of spinal nerves are further protected from lateral traction by wedging of a cone of dura surrounding the nerve root–spinal nerve complex into the intervertebral foramen.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PERIPHERAL NERVE INJURY
Severity of Peripheral Nerve Injury
The primary determinants of prognosis of peripheral nerve injury (PNI) are the severity of the injury and the residual integrity of the axons. PNI severity is typically classified according to the relative degree of axonal disruption. Proximal axonal lesions (ie, close to the cell body) are traditionally believed to be more severe than distal axonal lesions (ie, closer to the innervation target) as the likelihood for einnervation and recovery appears to vary indirectly with the distance between the location of the axonal lesion and the target tissue.
The two most commonly used anatomical classifications are the Seddon and Sunderland classifications (Table 1). The more commonly used classification in clinical practice is the three-tier Seddon classification, which includes (from mild to severe) neuropraxia, axonotmesis, and neurotmesis. Neuropraxia refers to damage to the myelin sheath typically associated with nerve stretching or compression where the axons and supporting elements (endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium) remain intact. The prognosis for a neuropraxic injury is favorable, with complete recovery of function occurring within weeks to months.
TABLE 1. Classification of nerve injury.
| Seddon3 | Sunderland4 | Processes | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuropraxia | 1 | Myelin damage Conduction slowing and blocking | Good |
| Axonotmesis | 2 | Loss of axonal continuity; endoneurium intact No conduction | Fair |
| Neurotmesis | 3 | Loss of axonal and endoneurial continuity; perineurium intact No conduction | Poor |
| 4 | Loss of axonal, endoneurial, and perineurial continuity; epineurium intact No conduction | ||
| 5 | Complete nerve transection No conduction |
NYSORA Tips
Most postoperative neurological symptoms associated with regional anesthesia tend to follow a neuropraxic pattern of injury and recovery.
Axonotmesis refers to axonal injury associated with fascicular impalement, nerve crush, or toxic injury, with damage to the endoneurium and possibly to the perineurium (Figure 13). Recovery following axonal loss may be prolonged and variable, depending on the extent (partial or complete) of disruption to the perineurium and on the distance from the injury site to the corresponding muscle.
Finally, neurotmesis refers to complete transection of the nerve, including the axons, endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurial connective tissue. It typically requires surgical intervention. The prognosis is often poor.
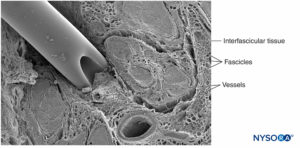
FIGURE 13. Human tibial nerve. In vitro puncture of nerve with neurostimulation needle. Scanning electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
Mechanisms of Injury
The mechanism of PNI related to the use of PNBs falls into one of three broad categories: mechanical and injection injury (traumatic), vascular (ischemic), and chemical (neurotoxicity). Most information on peripheral nerve injection injury are obtained from experimental research in animal models. Because such research is not possible in humans, mechanisms of PNI are not fully understood. This is because animal models significantly vary in species used, nerves injected, and study protocols, making it difficult to readily extrapolate such data to actual clinical practice.
Mechanical and Injection Injury
Mechanical or traumatic injury includes compression, stretch, laceration, or injection injury. Nerve compression or entrapment may produce a conduction block and, if prolonged, a focal demyelination of some axons. Needle trauma and other mechanical insults to nerves result in an increase in neuropeptide production and dorsal horn activity. Needle-related nerve compression can result from forceful needle-nerve contact from an approaching needle or injection inside the nerve itself. It has been postulated that an intraneural injection may lead to sustained high intraneural pressure, which, when exceeding capillary occlusion pressure, may lead to nerve ischemia and potentially injury.
Inadvertent injections of antibiotics, steroids, bovine collagen, botulinum toxin, and local anesthetics into peripheral nerves have all been associated with deleterious neurologic deficits. In a cadaveric model of deliberate intraneural injection of the sciatic nerve, the needle tip disrupted 3% of axons. Although some degree of axonal injury may potentially occur even in the absence of injury to the perineurium, the actual anatomical site of injury (eg, injection) is critical prognostically. One of the main causes of block-related PNI is injection of local anesthetic into a fascicle, causing direct needle and injection trauma, rupture of perineurium, and loss of the protective environment within the fascicle with consequent myelin and axonal degeneration. Stretch injuries to the nerves may result when nerves or plexi are placed in a nonphysiologic or exaggerated physiologic position. Finally, mechanical injury from laceration results when the nerve is injured by a needle, with the potential for spontaneous recovery most unlikely following complete transection. Table 2 indicates the evidence-based recommendations to reduce the risk of block-related PNIs.
TABLE 2. Evidence-based recommendations to reduce the risk of block-related PNI.
| Intraneural needle insertion may not always lead to nerve injury. |
| Intrafascicular needle placement and injection should be avoided. |
| Neither the presence nor the absence of a paresthesia during needle advancement or on injection of local anesthetic is entirely predictive of nerve injury. |
| Elicitation of severe pain during needle advancement or on injection of local anesthetic should prompt cessation of injection. |
| Presence of an evoked motor response at a current of less than 0.5 (0.1 ms) indicates intimate needle-nerve relationship, needle-nerve contact, or intraneural needle placement. This information is useful in clinical decision-making. |
| Injection pressure monitoring can detect injection into a poorly compliant tissue space, such as a nerve fascicle. |
| Ultrasound can detect intraneural injection, although such detection may occur too late to prevent injury as a small quantity of injectate is sufficient to rupture the fascicle. |
| Current ultrasound technology does not have adequate resolution to discern between an interfascicular and an intrafascicular injection. |
| Adequate images of needle-nerve interface are not consistently obtained by all operators and in all patients. |
Vascular Injury
Damage to the nerve vasculature during nerve blocks can result in local or diffuse ischemia and occurs when there is direct vascular injury, acute occlusion of the arteries from which the vasa nervorum are derived, or from hemorrhage within a nerve sheath. The epineurial circulation is a critical component of the overall neural circulation, and its removal reduces nerve blood supply by 50%. In most circumstances, no single vessel dominates the pattern over an entire length of nerve; however, the sciatic nerve is an exception to this rule, receiving its major arterial supply in the gluteal region from the arteria comitans nervi ischiadici.
NYSORA Tips
Vascular supply of the sciatic nerve is less abundant than the supply of most other peripheral nerves. This may explain the clinical observation regarding why addition of epinephrine to local anesthetic appears to prolong sciatic block significantly longer than for most other PNBs.
Nerves with an abundance of connective tissue may be less susceptible to compression because external forces are not transmitted directly to epineurial vessels. Local anesthetics and adjuncts potentially reduce neural blood flow in an agent- and concentration-dependent manner. Epinephrine has the potential to cause local vasoconstriction, but its role in causing nerve ischemia and injury is controversial. Trauma from injection may compromise blood flow further. Neural ischemia may also occur following disruption of the intrafascicular microvasculature, high injection pressures, tourniquets, and other compressive insults. Factors regarding inadvertent vessel puncture, resulting in the formation of an internal or external hematoma that can mechanically compress the fascicles from within or outside the nerve sheath and cause nerve inflammation, have been implicated in neurologic injury.
Chemical Injury
Chemical nerve injury results from tissue toxicity of injected solutions (eg, local anesthetics, alcohol, or phenol) or its additives. The toxic solution may be injected directly into the nerve or into adjacent tissues, causing an acute inflammatory reaction or chronic fibrosis that indirectly involves the nerve. Much of the research on neurotoxicity of local anesthetics has been done in in vitro models, particularly with intrathecal application.
There is evidence that nearly all local anesthetics can have myotoxic, neurotoxic, and cytotoxic effects in various tissues under certain conditions; however, local anesthetics vary in their neurotoxic potential. Several studies have demonstrated that local anesthetics can lead to fragmentation of DNA and disrupt the membrane potential in mitochondria, resulting in the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation, which may result in apoptosis. There is also a direct correlation between concentration of the local anesthetic and duration of exposure to the nerve, with death of Schwann cells, infiltration with macrophages, and myelin damage. Some local anesthetics have an intrinsic vasoconstrictive effect that can decrease blood flow to the nerves, potentially resulting in ischemia and injury.
However, the inherent difficulty in extrapolating these laboratory studies to the clinical practice of modern PNBs is that there is a substantial decrease in the concentration of local anesthetics by the time it reaches the axons.
The site of local anesthetic application (extraneural, intraneural, interfascicular, intrafascicular) (Figures 12, 14, and 15) may be the primary determinant of whether neurotoxicity will occur, especially if the concentration is high and duration of exposure prolonged. Most chemical substances, including all local anesthetics, injected intrafascicularly lead to severe fascicular injury, whereas the same substances injected intraneurally but interfascicularly cause less injury or no detectable injury at all. Indeed, needle penetration of a nerve may result in minimal damage if it is not combined with local anesthetic injection within the nerve fascicle.
FIGURE 14. Overlap of the needle in the supraclavicular brachial plexus. If the neurostimulation needle pierces the nerve, as compared with the static images, the needle injures the fascicles. Different approaches are shown in A. and B. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
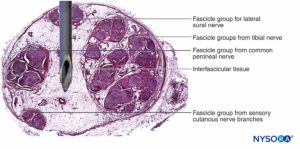
FIGURE 15. Overlap of the needle in the sciatic nerve, posterior approach. If the neurostimulation needle pierces the nerve, based on the static images, the needle injures the fascicles. Observe the difference in size between the needle and fascicles. If there is a large amount of interfascicular tissue, as occurs within the sciatic nerve, the risk of fascicular injury is reduced. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
In a rodent model, Whitlock demonstrated that intrafascicular injection of 0.75% ropivacaine resulted in severe histological abnormalities, including demyelination, axonal degeneration, and Wallerian degeneration. However, extrafascicular injection of 0.75% ropivacaine also resulted in axonal injury, although reduced in severity. Farber and colleagues recently reported that all commonly used local anesthetics (bupivacaine, lidocaine, and ropivacaine) produced nerve injury when injected intrafascicularly. In their study, the degree of injury decreased with increasing distance from site of injection. Of note, even administration of saline intrafascicularly resulted in intermediate damage to nerves, indicating a baseline level of injury associated with injecting any agent into a nerve.
NYSORA Tips
While the clinical importance of neurotoxicity remains controversial, the location of the needle tip during injection of the local anesthetic plays a crucial role in determining the likelihood and severity of nerve injury.
Inflammatory Injury
Inflammatory mechanisms of PNI are being increasingly recognized as an important mechanism in post-PNBs neurologic deficit. Nonspecific inflammatory responses targeting peripheral nerves can occur either remote from the site of surgery or within the operative limb, where it may be difficult to distinguish from other causes of PNI. Inflammatory mechanisms have been proposed as responsible for persistent phrenic nerve injury following interscalene block for shoulder surgery (Figure 12). Kaufman and colleagues reported a series of 14 patients with chronic diaphragmatic paralysis following interscalene block.
During surgical exploration, adhesions, fascial thickening, vascular changes, and scar tissue (present in 10 of 14 patients) involving the phrenic nerve suggested chronic inflammation and were consistent with compression neuropathy. Recent research suggested that intrathecal and intraneural injection of ultrasound gel can also lead to inflammation in the subarachnoidal and peripheral nerves, respectively.
ETIOLOGY OF NERVE INJURY FOLLOWING PERIPHERAL NERVE block
Anesthetic Factors
Several studies have reported that the type of anesthesia (regional vs general) does not appear to influence the incidence of PNI. The University of Michigan performed a retrospective analysis of PNI and did not identify PNB as an independent risk factor for PNI in their series. Three epidemiologic studies from the Mayo Clinic reported that regional anesthesia does not increase the risk of PNI following total knee arthoplasty (TKA), total hip arthroplasty (THA), and total shoulder arthroplasty. Recent surgical literature suggested that the risk of postoperative neurologic injury associated with PNB may be higher than that reported in anesthesia literature. We discuss several technical factors related to PNB that may increase the risk of PNI.
Intraneural Injection
Avoidance of deliberate trauma to nerves, including intraneural injection, is probably a key safety principle of regional anesthesia. However, intraneural injection may occur in clinical practice without resulting in overt signs of nerve injury. In fact, unintentional intraneural (but probably extrafascicular) epineurial injection may be more common than previously recognized. The presumed risks of intraneural injection have been challenged by Bigeleisen and colleagues, who reported that nerve puncture and apparent intraneural injection during axillary brachial plexus block in healthy patients did not lead to neurologic injury. A larger study by Liu recruited 257 young, healthy patients having ultrasound-guided interscalene or supraclavicular block for shoulder surgery. The incidence of unintentional intraneural injection was 17% without any occurrence of PNI. However, clinical experience is limited, and the sample sizes of current studies are inadequate to capture infrequent events, such as nerve injury. In contrast, in a case report by Cohen, PNI occurred following intraneural injection during ultrasound-guided interscalene block.
Unfortunately, reports of intraneural injection do not inform us regarding sites of injection in relation to fascicles. Distinguishing the outer epineurium of a peripheral nerve from surrounding tissues using ultrasound imaging is challenging.
Orebaugh performed mock interscalene injections (albeit with small volumes) in a cadaver model. Ultrasound imaging cannot differentiate extrafascicular and intrafascicular neural components over the range of locations that PNB is performed. Furthermore, an injection adjacent to the outer epineurium may generate a halo similar in appearance to an intraneural injection, making it difficult to discern hazardous from nonhazardous needle placement. Importantly, only a small amount of local anesthetic (eg, 0.1–0.5 mL) is sufficient to rupture the fascicle and its perineurium.
NYSORA Tips
Relying on observation of nerve swelling on ultrasound during PNBs as a monitoring method is inadequate for detection of intrafascicular injection and injury prevention.
Most recent experimental and clinical data suggest that PNI from local anesthetic injection into the nerve occurs and remains a real clinical danger. The sequelae from such an injury may be long lasting and require surgical intervention.
Proximal Versus Distal PNBs and Risk of Neurologic Injury
The PNB injections at more proximal sites (ie, roots of brachial plexus vs peripheral nerves of the brachial plexus) (Figures 9, 10, and 11) may be at higher risk of nerve injury compared to distal sites of PNB. This is likely due to differences in neural architecture, primarily the ratio of neural versus nonneural (connective) tissue (Figure 16). Clinically, intraneural injection into the extrafascicular connective tissue within the epineurium may not result in nerve injury. This is consistent with experimental work that has correlated intrafascicular injection to peripheral nerve injection injury.
The structural organization of the peripheral nerve provides insight into the relative risk for mechanical injury among different nerves or even at different locations within the same nerve (Figure 16). Because the epineurium is typically a tougher layer than the surrounding adipose tissue, nerves tend to be “pushed away” by an advancing needle, rather than penetrated.
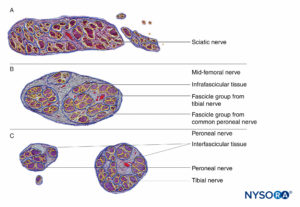
FIGURE 16. Transversal section of sciatic nerve at subgluteal region (A), mid-femoral region (B), and tibial and peroneal nerves at popliteal region (C). (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
Similarly, when the epineurium is penetrated by a needle, the needle tip and injection are much more likely to enter the interfascicular adipose tissue than the fascicles (Figure 15). The adipose tissue within the epineurium allows the fascicles to escape the advancing needle; however, this protection may be undermined by abrupt needle advancement needle or forceful needle-nerve contact. The nerves characterized by tightly packed fascicles and high fascicular-to-connective tissue content may be at greater risk of mechanical nerve injury than those characterized by lower fascicular-to-connective tissue content.
Relatively high incidences of transient neurologic sequelae are reported following interscalene block, where there is a 1:1 ratio of neural to nonneural tissue (Figure 12). Several studies documented a rather high incidence of neurologic symptoms after brachial plexus block, but without severe sequelae. In other studies, there were low absolute numbers of upper extremity PNB-related neurologic complications, rendering any comparison of outcomes at proximal sites with distal sites problematic.
Injury rates following lower extremity PNB have been reported as 0.41% (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.02–9.96) in the gluteal region, compared with 0.24% (95% CI, 0.10–0.61) in the popliteal region, indicating no significant difference. It is possible that many of the neurologic symptoms reported by the patients postoperatively after PNBs are inflammatory and due to needle-nerve contact or forceful injection, leading to intraneural inflammation, leading to symptoms, as demonstrated by Steinfeldt. Therefore, the wisdom in Selander’s teaching that “nerves should be handled with care” remains relevant.
Needle Type
Needle-tip characteristics influence the likelihood of fascicular penetration and nerve injury. Long-bevel needles are more likely to puncture and enter the fascicle compared with short-bevel needles; however, short-bevel needles appear to cause more damage in case of fascicular penetration (Figure 17). The severity of nerve injury after needle-nerve perforation is also linked to the needle diameter; however, no such difference exists with regard to extent of inflammation after needle-nerve trauma.
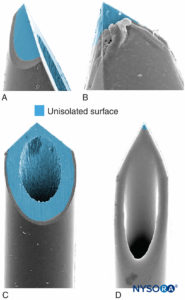
FIGURE 17. Presented is 21-gauge neurostimulation, peripheral needle type A (A and B) and type D (C and D). Scanning electron microscopy. (Reproduced with permission from Reina MA: Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.)
The effect of needle design on the likelihood and severity of mechanical nerve injury has been extensively debated. It is not surprising that mechanical needle trauma and intraneural injection are key mechanisms in iatrogenic nerve injury, such as with regional anesthesia. For example, in the setting for neuraxial anesthesia, the dural lesions produced by different needle types vary greatly in morphology; a Whitacre needle produces a more traumatic opening, with tearing and severe disruption of the collagen fibers, than a Quincke-style needle. Similarly, the likelihood and extent of mechanical injury to nerve fascicles following intraneural injection during PNB also depend on needle-tip design. It seems intuitive that short-bevel needle types are less likely to penetrate the protective connective tissue layers of the peripheral nerves (epineurium, perineurium). Indeed, Selander and colleagues documented that a needle with a 45° bevel is much less likely to penetrate perineurium and inflict fascicular injury than a needle with a 15° bevel. However, should a nerve fascicle become accidentally impaled during a nerve block procedure, the lesions induced by short-bevel needles may be more severe and take longer to repair than those induced by long-bevel needles.
Surgical Factors
Surgical Positioning Requirements
Neurologic complications can occur following positioning for surgical requirements. Mechanisms of nerve injury related to surgery include traction, transection, compression, contusion, ischemia, and stretch. Regardless of mechanism, the final pathway of nerve injury may include the following factors: physical disruption of intraneural blood vessels causing patchy ischemia or hemorrhage; elevated intraneural venous pressures; endoneurial edema; impairment of axoplasmic flow; Schwann cell damage; myelin displacement; axonal degeneration; and Wallerian degeneration. During surgery, patients are placed in positions they would not otherwise tolerate unless anesthetized. In addition, the physical forces required during surgery (eg, placement of prostheses) can be excessive, potentially stressing anatomical structures remote from the surgical site, including the vertebral column.
In a closed-claims analysis, 9 of 53 anesthetic-related brachial plexus injuries were related to intraoperative positioning (shoulder braces in the head-down position [three claims], patient’s arm suspended on a bar [two claims], and other malpositions [four claims]). Only two claims were related to a regional anesthesia technique.
Effects of the Pneumatic Tourniquet
Tourniquet inflation causes nerve damage by mechanical deformation or ischemia. The main features of tourniquet neuropathy include weakness or paralysis, diminished touch, vibration and position sense, and preserved senses of heat, cold, and pain. In an experimental model, tourniquet compression resulted in increased vascular permeability, intraneural edema, and sciatic nerve degeneration.
For instance, tourniquet compression during meniscectomy surgery can lead to femoral nerve denervation and delayedfunctional recovery. Wider tourniquets, using lower cuff pressures, and limiting the duration of inflation have been proposed as methods to prevent tourniquet neuropathy.
Postsurgical Inflammatory Neuropathy
Patients with postsurgical inflammatory neuropathy typically present with a neuropathy that is delayed in onset and remote from the surgery. The neuropathies are focal and multifocal with pain and weakness. An inflammatory-immune mechanism is responsible, and there is evidence of axonal degeneration and lymphocytic-mediated inflammation.
NYSORA Tips
Not all episodes of PNI are mechanical in origin.
Patient Factors
Preexisting Neuropathy
A preoperative neurologic deficit or neural compromise, whether from nerve entrapment or metabolic, ischemic, toxic, hereditary, and demyelination reasons, may be present in patients presenting for surgery. Many of these preexisting neurologic conditions are subclinical, yet they may be associated with increased risk of PNI postoperatively. For instance, often-overlooked, but common, cervical spondylosis may result in rough and irregular opening of the intervertebral foramen.
The spinal nerve–nerve root complex becomes subject to repeated trauma, resulting in fibrosis reducing its mobility. The spinal nerve–nerve root complex is consequently at increased risk of traction injury during upper extremity movement and positioning. The ulnar nerve may become entrapped in the cubital tunnel at the elbow or at the wrist. Risk factors for perioperative ulnar neuropathy include male gender, extremes of body habitus, and prolonged admission.
Diabetic neuropathies are common and represent a wide range of clinical entities commonly resulting in distal symmetric sensory polyneuropathy. Asymmetric diabetic neuropathies comprise acute or subacute proximal motor neuropathy (often painful), cranial neuropathy, truncal or thoracoabdominal neuropathy (often painful), and entrapment neuropathy in the limbs. Diabetic lumbar radiculopathy can present with pain radiating from the back to the lower limbs and mild weakness.
There may be diffuse neuropathy with abnormal electromyography of paraspinal muscles and muscles innervated by the sacral plexus, gluteal, femoral, and sciatic nerves. Elderly patients with diabetes may have combined proximal and distal involvement, placing these patients at increased risk of PNI. Diabetic nerve fibers may be more susceptible to toxic effects of local anesthetics because of chronic ischemic hypoxia and because nerves are exposed to larger concentrations of local anesthetics related to decreased blood flow. The occurrence of PNI following neuraxial block in patients with diabetic neuropathy has been reported as being higher (0.4%; 95% CI, 0.1%–1.3%) than the general population; however, its true clinical relevance is controversial as many of these patients are among the greatest beneficiaries of PNBs.
Similarly, the actual risk of PNBs in the setting of severe peripheral vascular disease, vasculitis, cigarette smoking, and hypertension is not known. Regardless, patients with these conditions could be more vulnerable to further ischemic insults during the perioperative period, similar to patients with alcohol- and cisplatin-induced neuropathies. Patients with multiple sclerosis and hereditary neuropathy may have subclinical preoperative neural compromise within the peripheral nervous system.
Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis may exaggerate a peripheral injury, adversely affecting physical recovery. Spinal canal stenosis is a risk factor for common peroneal palsy following THA and may be significant in cases of paraplegia or cauda equina syndrome following epidural anesthesia. Hebl documented new or progressive neurologic deficits following neuraxial anesthesia in patients with preexisting spinal canal stenosis or lumbar disk disease. Overall, 10 (1.1%, 95% CI 0.5%–2.0%) patients developed new deficits or worsening of preexisting symptoms. The frequency of complications was higher in patients who had compressive radiculopathy or multiple central neuraxial diagnoses. However, it is likely that there were multiple etiological factors because deficits often correlated with the side of preexisting pathology or surgical procedure. A summary of anatomical, anesthetic, surgical, and patient factors contributing to PNI is listed in Table 3.
TABLE 3. Summary of anatomical, anesthetic, surgical, and patient factors contributing to perioperative nerve injury.
| Factor Potentially Contributing to or Relevant to PNI | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| Anatomical | Internal morphology of nerve, including connective tissue supporting fascicles and axons1,63 | Epineurial tissue may offer protection from direct trauma and external compression |
| Gross anatomical factors: location, course, relations, attachments, and relative mobility of nerves1 | — | |
| Specific structures are at risk | Examples: ulnar nerve at elbow,76,99 CPN 81,100,101 | |
| Anesthetic | Type of anesthesia | EA and GA but not PNB were associated with PNI.47 PNB not associated with PNI following TKA,48 THA,49 or TSA.50 |
| Insensate limb | Places nerves at risk from compression or stretching76 | |
| Site of PNB: proximal at increased risk versus distal PNB | Not supported by clinical evidence | |
| Level of sedation during nerve block | Continues to be controversial. However, with objective monitoring of needle-nerve relationship and disposition of injectate (US, nerve stimulation, opening injection pressure monitoring), this issue is likely to become mute. For latest published recommendation, consult ASRA practice Advisory | |
| Mechanical trauma from needle, catheter, or injectate | — | |
| Direct local anesthetic toxicity | Time and concentration dependent; risk with intrafascicular greater than extrafascicular exposure6,15 | |
| Neural ischemia | Secondary to compression,76 vasoconstrictors,19,20 intrafascicular injection,54 tourniquet82,103 | |
| Surgical | Trauma: contusion, compression, retraction, traction, transection | |
| Perioperative positioning76 | ||
| Tourniquet: duration of inflation and pressure81,104 Swelling, plaster casts Specific procedures have unique risk profile95 | Associated with marked clinical deficits80 and pathological changes on EMG84 Risks of PNI following TKA,48 THA,49 and TSA50 were 0.79%, 0.72%, and 2.2%, respectively |
|
| Patients | Preoperative neural compromise theoretically increases risk of PNI | Etiology includes entrapment, metabolic, ischemic, toxic,93 hereditary, and demyelination causes94 |
| Lumbar canal stenosis | May be significant risk factor following neuraxial block96,98 | |
| Other | Inflammatory mechanism | Nonmechanical cause physically and temporally remote from PNB43 |
MONITORING NEEDLE-NERVE DISTANCE DURING PNBS AND PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS
While the risk of needle-nerve contact, intraneural needle placement, and intraneural injection has recently been questioned in small clinical series where overt injuries did not occur, PNB-related nerve injuries continue to be reported. Susan MacKinnon’s team has recently sternly warned against intentional intraneural injection based on their results of neurotoxicity following intrafascicular injections of local anesthetics.
This publication in one of the premier journals in the specialty (Anesthesia and Analgesia) specifically warned against the recent recommendations by some providers that intraneural injection is without risk and, in fact, can be beneficial for block quality.
It is important to note that MacKinnon’s team’s warning stems from decades of clinical practice of peripheral nerve repair surgery and over 350 scientific publications on the subject. Although the incidence of PNB-related nerve injuries is relatively uncommon, they are among the most common disabling complications related to administration of anesthesia and are likely underreported in the literature due to medicolegal and institutional reputation-related implications. The potentially devastating impact of a severe nerve injury on the patient’s quality of life mandates a systematic approach to mitigating the risk through standardization of injection techniques.
Mechanical Elicitation of Paresthesias
The association between the mechanical elicitation of paresthesias and consequent PNI has been the subject of debate for a long time. While some large observational trials have indeed implicated the elicitation of paresthesias as a risk factor for PNI, such an association has not been supported by others. Moreover, the occurrence of paresthesias is not a sensitive sign of needle-nerve contact, as only 38% of patients experienced paresthesias during real-time visualization of needle-nerve contact.
Therefore, the absence of paresthesias during the performance of a nerve block does not reliably exclude needle-nerve contact, and nerve injury has been reported both in patients who have experienced severe paresthesias and in those experiencing no paresthesias during the PNB procedure. Regardless, a severe paresthesia, or pain on needle advancement or injection, may indicate intraneural needle placement and, when present, should prompt cessation of injection and needle repositioning.
If and how the use of deep sedation influences patients’ perception and interpretation of the paresthesia as a symptom has not been studied. Likewise, ultrasound-guided PNBs often involved multiple injections of aliquots of local anesthetic in several different anatomical areas. It is not known how the spread of the local anesthetic during multiple-injection techniques and the incipient sensory block that occurs during the procedure may have an impact on the value of paresthesia as a safety monitor.
Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
Motor response to peripheral nerve stimulation relies on Coulomb’s law, whereby a smaller current intensity (mA; or, more correctly, electrical energy) is required to elicit a motor or sensory response as the needle tip approaches the nerve.
The importance of avoiding injection when motor response is obtained by very low current intensity (<0.2 mA) and risk of nerve injury was first reported by Voelckel and colleagues. Histological nerve injury occurred in 50% of the pigs when motor response was obtained at less than 0.2 mA, compared to no histological changes at 0.3–0.5 mA. Presence of motor response at less than 0.2 mA has been shown to be a specific but not sensitive indicator of intraneural needle placement in both animals and humans.
Peripheral nerve stimulation as a nerve localization technique is characterized by relatively low sensitivity but high specificity for predicting relative needle-nerve proximity, suggesting that such a response actually reflects needle-axon distance. Both experimental data and clinical reports have shown that an evoked motor response may not be reliably elicited when the needle is placed in the immediate vicinity of the nerve or even intraneurally. However, the same research indicated that when a motor response is elicited at low current intensity (eg, < 0.5 mA, 0.1 ms), the needle tip is invariably positioned on the nerve or within the nerve. Importantly, peripheral nerve stimulation has withstood the test of time, as evidenced by the largest published data sets related to PNI, all of which relied primarily on peripheral nerve stimulation to achieve safe and successful PNB.
Opening Injection Pressure Monitoring
The association between high injection pressures and intrafascicular injection was first described in 1979 by Selander and subsequently studied in several animal models. In a dog model, an intentional intrafascicular injection was associated with both high opening injection pressure (≥25 psi) and corresponding clinical and histological nerve injury. In contrast, extrafascicular injections were not associated with high injection pressures or with nerve injury. In another study in a dog model, high injection pressure (≥20 psi) was also associated with intrafascicular injection as well as clinical and histological nerve injury, while intraneural but interfascicular injection was associated with low injection pressure (<10 psi) and no neurologic or histologic consequences. During intraneural injection into the median nerves of pigs, Lupu and colleagues were unable to detect a significant correlation between the maximum pressure generated and clinical or histological nerve injury. In this study, peak injection pressures were well below 25 psi, yet 7 of 10 nerve specimens had evidence of axonal damage on histological examination. In one case, axonal damage ensued following a maximum injection pressure of only 2.2 psi. Importantly, functional deficits measured up to 7 days postinsult were absent in all 10 pigs studied. More recently, in the first such study in human tissue, Orebaugh and colleagues reported that 100% of injections directly into the roots of the brachial plexus of fresh human cadavers resulted in high injection pressures (>30 psi), with one occurrence of injectate spread into the epidural space. Importantly, analysis of the attained injection pressure curves indicated that all injections into the brachial plexus roots were associated with pressures greater than 15 psi.
Similar data on the injection pressure–nerve relationship were reported by Krol et al in the peripheral nerves. In a study on pressure monitoring during injections for median, radial, and ulnar nerve PNBs in fresh human cadavers, the authors reported significant differences between intraneural and perineural injection pressures. Intraneural injection pressures showed low specificity but high sensitivity with intraneural needle placement.
Several studies have utilized injection pressure as a monitoring tool for intraneural (intraepineurial) injection during sciatic nerve block without complications. Robards and colleagues studied 24 patients, who each received an injection inside their sciatic nerve at the level of the popliteal fossa. Injection pressures of less than 20 psi were recorded in 20 patients, while injection pressures greater than 20 psi were observed in the remaining 4 patients, prompting cessation of the injection; none of the patients suffered any neurologic dysfunction, suggesting that injections that occurred intraneurally were extrafascicular.
In a study of intraneural stimulation thresholds during ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus blocks, Bigeleisen and colleagues reported a combination of high resistance to injection, low current stimulation, and pain on injection coincided in two patients with an intraneural needle placement that necessitated needle repositioning before completing the injection without complications.
Beyond the risk of neurologic injury, high injection pressures can lead to several other unwanted effects or serious complications. For instance, Gadsden and colleagues reported that high injection pressure during lumbar plexus block carries a risk for epidural spread (Figures 18 and 19). In this study, injection pressures greater than 20 psi during lumbar plexus block led to unacceptable risk of high-level epidural block, in some patients as high as the T3 level, necessitating early termination of the study for safety reasons.
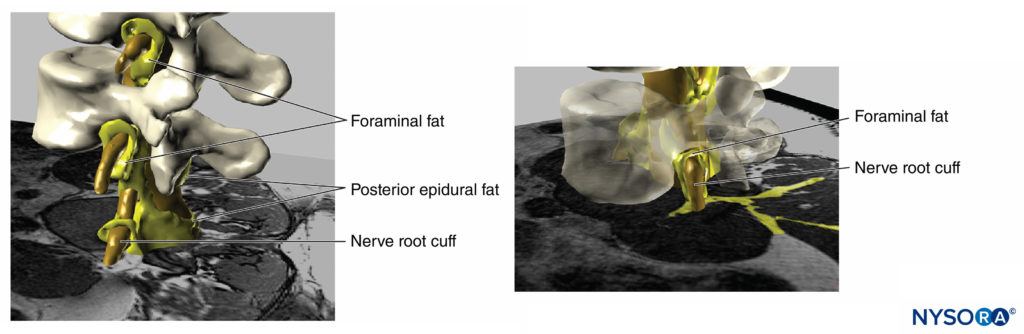
FIGURE 18. Three-dimensional reconstruction of MRI image of vertebrae, dural sac, epidural fat and foraminal adipose tissue. The yellow painted areas represent interconnections between the adipose tissues which can serve as potential paths for spread for injected solutions. (Used with permission from M.A. Reina.)
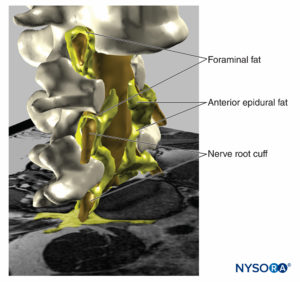
FIGURE 19. Three-dimensional reconstruction of vertebrae, dural sac, epidural fat, and foraminal fat from magnetic resonance images of a patient. We can see the potential pathway through the fat from epidural fat, foraminal fat, to other fat compartments, as the fat envelops the nerve roots outer the foraminal canal of the spine or the fat found among the muscular fascias. Two vertebral bodies were removed, allowing visualization of epidural fat in the anterior epidural space. (Used with permission from M.A. Reina.)
More recently, Gautier et al reported that high injection pressure during interscalene injection can lead to substantial epidural spread of the injectate. Gautier’s report offered an explanation for the precipitous respiratory and cardiovascular demise occasionally reported immediately following interscalane block, as well as suggested that injection force/pressure should be monitored during the injection process. Assessment of injection pressure (resistance) during PNB is of increasing interest to clinicians and researchers. This is not surprising, given that injection into densely packed nerve fascicles requires more force to initiate an injection (opening pressure) than perineural or intraneural-interfascicular injections into the loose perineural or perifascicular connective tissue (Figures 12, 14, and 15).
In an attempt to standardize monitoring and documentation of nerve block procedures, a group of North American experts suggested documenting the resistance to injection as one of the elements of the standard clinical note. However, two independent groups found that the clinician’s accuracy in gauging injection pressure or the tissue being injected is limited when using a subjective, syringe feel technique, thus questioning the reliability of subjective assessments. In the meantime, several means of monitoring injection pressures have been recommended.
Taken together, the data to date suggest that high opening injection pressure can detect an intrafascicular injection, but not an intraneural interfascicular injection. In the first study in patients, Gadsden and colleagues demonstrated that opening injection pressure with the needle tip at 1 mm away from the nerve roots of the interscalene brachial plexus was consistently lower than 15 psi (mean peak pressure 8.2 ± 2.4 psi). In contrast, opening injection pressure during needle-nerve contact was 15 psi or more (mean peak pressure 20.9 ± 3.7 psi) in 35 of 36 injections. In this study, aborting the injection when opening injection pressure reached 15 psi reliably prevented commencement of injection in 97% cases of needle-nerve contacts. In addition, high opening injection may correlate well with other indices of needle-nerve contact, such as low current stimulation and paresthesia on injection.
In a follow-up study, Gadsden et al used similar methodology to determine whether high opening pressure can also detect needle-nerve contact in peripheral nerves, such as the femoral nerve. The researchers reported that high opening injection pressure consistently detected (97%) needle-nerve contact and prevented an injection against the femoral nerve or fascicles. Moreover, their research suggested that high opening injection pressure can detect insertion of the needle into a wrong tissue plane. In this report, inability to inject local anesthetic with opening injection pressure below 15 psi detected 100% of instances of the needle placement on the wrong aspect of the fascia iliaca.
Further research is needed to determine the clinical benefits of routine injection pressure monitoring and actual “safe” opening injection pressure values for various nerve block procedures. Regardless, sufficient data exist to suggest that monitoring opening injection pressure during interscalene and femoral nerve blocks adds additional critical safety information that can influence clinical decision-making. Injection pressure monitoring may prove to be most useful for its negative predictive value for functional nerve injury, as no cases of clinically significant neuropathy have been reported in the literature with low injection pressures. Based on the available data, avoidance of high resistance and opening injection pressure greater than 15 psi appears to be a prudent strategy. At the very least, this is because during nerve block injections, the injections into the loose perineural connective tissue should never require more than 15 psi; therefore, when opening pressure of 15 psi is reached before injection actually occurs, the operator has an opportunity to reposition the needle away from the nerve before injection into possibly the wrong tissue space or vulnerable parts of the nerve (fascicles, needle-nerve contact).
Electrical Impedance
Electrical impedance monitoring measures the resistance to flow of an alternating current in an electrical circuit and could be added to the existing nerve stimulators. Electrical impedance is sensitive to changes in tissue composition, particularly water content. In a pig sciatic nerve model, Tsui and colleagues demonstrated that nerves have greater electrical impedance than the surrounding muscle and interstitial fluid due to their low water and high lipid content. They found that the electrical impedance increased abruptly on entrance into the intraneural compartment relative to the extraneural compartment. The absolute value at which intraneural needle placement occurred could not be determined because of substantial variance within the data.
While electrical impedance monitoring appears promising to detect intraneural needle tip placement, it necessarily implies that nerve puncture must occur before a change in impedance is detected. There is also reasonably strong evidence that measurement of electrical impedance can differentiate intravascular from perineural placement of a needle when 5% dextrose in water is injected before performance of the block. Based on the currently available data, impedance monitoring can differentiate between certain tissues, such as muscle and adipose/connective tissue. However, the variability of impedance measurements among different nerves or even the same nerves at different locations requires further research before any recommendations regarding the potential clinical applicability of this modality can be made.
Ultrasound
Although ultrasound can detect intraneural injection, the widespread use of ultrasound guidance has not decreased the rate of PNI. In animals, ultrasound is sensitive enough to detect as little as 1 mL of injectate; however, a much smaller amount of injectate is sufficient to injure the fascicles.
Regardless, no animal or human study to date has definitively demonstrated an association between real-time sonographic visualization of intraneural injection of local anesthetic and consequent functional (or otherwise clinically important) nerve injury. One reason may be that the resolution of the current ultrasound machines produced is not high enough to differentiate potentially hazardous intrafascicular injection from injection into the potentially more forgiving extrafascicular compartment.
In addition, the ability to interpret such images is highly user dependent, and the ability to obtain high-definition, quality images varies among patients. The use of ultrasound guidance has substantially facilitated the teaching and popularized the utilization of PNBs while decreasing the incidence of systemic toxicity of local anesthetics. However, in studies to date, ultrasound has not decreased the incidence of PNI. More information about ultrasound and monitoring is covered in Monitoring, Documentation, and Consent for Regional Anesthesia Procedures.
NYSORA Tips
The main mechanisms of PNB-mediated injury include mechanical trauma, ischemia, local anesthetic toxicity, and inflammation. The main source of PNB-mediated neurologic complications is likely mechanical fascicular injury or injection of local anesthetic into a fascicle, causing myelin and axonal degeneration.
SUMMARY
Neurological complications associated with PNB are multifactorial and associated with a range of perioperative processes and patient, anesthetic, and surgical factors, The anatomy of peripheral nerves is variable in location, structure, and susceptibility to injury. The main mechanisms of PNB-mediated injury include mechanical trauma, ischemia, local anesthetic toxicity, and inflammation. The main source of PNB-mediated neurologic complications is likely mechanical fascicular injury or injection of local anesthetic into a fascicle, causing myelin and axonal degeneration. The reported incidences of neurologic complications following PNB vary significantly, and interpreting the literature is difficult because of varied study methodologies, including differences in the neurological outcomes captured. Fortunately, most postoperative neurological deficits appear to resolve with time, and the incidence of serious long-term neurologic complications attributable to PNB is relatively uncommon.
Avoidance of deliberate trauma to nerves, including intraneural injection, is a key safety principle of regional anesthesia. At this time, there is evidence that objective monitoring of needle placement and injection, such as ultrasound, nerve stimulation, and opening injection pressure, can help detect needle-nerve contact and intraneural needle placement. Although, as with many other monitors in clinical practice (eg, pulse oximetry), there is no evidence these monitors can reduce incidence of neurologic complications, there are data suggesting that their combination should confer additional safety during PNBs. Careful patient selection, combined use of more than one nerve localization technique or monitor, avoiding injection with opening injection pressure, and limiting the number of needle passes and injections where appropriate will further decrease the risk and make the practice of PNBs less of an art than a science.
REFERENCES
- Sunderland S: Nerve Injuries and Their Repair: A Critical Appraisal. Churchill Livingstone, 1991.
- Boezaart AP: That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as sweet—and its thorns would hurt as much. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2009;34:3–7.
- Seddon HJ: A classification of nerve injuries. Br Med J 1942;2: 237–239.
- Sunderland S: A classification of peripheral nerve injuries producing loss of function. Brain 1951;74:491–516.
- Brull R, McCartney CJ, Chan VW, El-Beheiry H: Neurological complications after regional anesthesia: contemporary estimates of risk. Anesth Analg 2007;104:965–974.
- Hogan QH: Pathophysiology of peripheral nerve injury during regional anesthesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2008;33:435–441.
- Burnett MG, Zager EL: Pathophysiology of peripheral nerve injury: a brief review. Neurosurg Focus 2004;16:E1.
- Steinfeldt T, Poeschl S, Nimphius W, et al: Forced needle advancement during needle-nerve contact in a porcine model: histological outcome. Anesth Analg 2011;113:417–420.
- Kerns JM: The microstructure of peripheral nerves. Techn Reg Anesth Pain Manag 2008;12:127–133.
- Gentili F, Hudson AR, Kline D, Hunter D: Early changes following injection injury of peripheral nerves. Can J Surg 1980;23:177–182.
- Whitlock EL, Brenner MJ, Fox IK, Moradzadeh A, Hunter DA, Mackinnon SE: Ropivacaine-induced peripheral nerve injection injury in the rodent model. Anesth Analg 2010;111:214–220.
- Mackinnon SE, Hudson AR, Gentili F, Kline DG, Hunter D: Peripheral nerve injection injury with steroid agents. Plast Reconstr Surg 1982; 69:482–490.
- Gentili F, Hudson AR, Hunter D: Clinical and experimental aspects of injection injuries of peripheral nerves. Can J Neurol Sci 1980;7:143–151.
- Sala-Blanch X, Ribalta T, Rivas E, et al: Structural injury to the human sciatic nerve after intraneural needle insertion. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2009;34:201–205.
- Gentili F, Hudson A, Kline DG, Hunter D: Peripheral nerve injection injury: an experimental study. Neurosurgery 1979;4:244–253.
- Hadzic A, Dilberovic F, Shah S, et al: Combination of intraneural injection and high injection pressure leads to fascicular injury and neurologic deficits in dogs. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2004;29:417–423.
- Selander D, Edshage S, Wolff T: Paresthesiae or no paresthesiae? Nerve lesions after axillary blocks. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1979;23:27–33.
- Selander D, Sjostrand J: Longitudinal spread of intraneurally injected local anesthetics. An experimental study of the initial neural distribution following intraneural injections. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1978;22: 622–634.
- Myers RR, Heckman HM: Effects of local anesthesia on nerve blood flow: studies using lidocaine with and without epinephrine. Anesthesiology 1989;71:757–762.
- Partridge BL: The effects of local anesthetics and epinephrine on rat sciatic nerve blood flow. Anesthesiology 1991;75:243–250.
- Rodriguez J, Taboada M, Garcia F, Bermudez M, Amor M, Alvarez J: Intraneural hematoma after nerve stimulation-guided femoral block in a patient with factor XI deficiency: case report. J Clin Anesth 2011;23:
234–237. - Ben-David B, Stahl S: Axillary block complicated by hematoma and radial nerve injury. Reg Anesth Pain Med 1999;24:264–266.
- Mackinnon SE, Hudson AR, Llamas F, Dellon AL, Kline DG, Hunter DA: Peripheral nerve injury by chymopapain injection. J Neurosurg 1984;61:1–8.
- Topuz K, Kutlay M, Simsek H, Atabey C, Demircan M, Senol Guney M: Early surgical treatment protocol for sciatic nerve injury due to injection—a retrospective study. Br J Neurosurg 2011;25:509–515.
- Amaniti E, Drampa F, Kouzi-Koliakos K, et al: Ropivacaine myotoxicity after single intramuscular injection in rats. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2006;23: 130–135.
- Beyzadeoglu T, Torun Kose G, Ekinci ID, Bekler H, Yilmaz C: Cytotoxicity of local anesthetics to rats’ articular cartilage: an experimental study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2012;46:201–207.
- Cereda CM, Tofoli GR, Maturana LG, et al: Local neurotoxicity and myotoxicity evaluation of cyclodextrin complexes of bupivacaine and ropivacaine. Anesth Analg 2012;115:1234–1241.
- Dragoo JL, Braun HJ, Kim HJ, Phan HD, Golish SR: The in vitro chondrotoxicity of single-dose local anesthetics. Am J Sports Med 2012;40:794–799.
- Mishra P, Stringer MD: Sciatic nerve injury from intramuscular injection: a persistent and global problem. Int J Clin Pract 2010;64:1573–1579.
- Nouette-Gaulain K, Dadure C, Morau D, et al: Age-dependent bupivacaine-induced muscle toxicity during continuous peripheral nerve block in rats. Anesthesiology 2009;111:1120–1127.
- Padera R, Bellas E, Tse JY, Hao D, Kohane DS: Local myotoxicity from sustained release of bupivacaine from microparticles. Anesthesiology 2008;108:921–928.
- Small SP: Preventing sciatic nerve injury from intramuscular injections: literature review. J Adv Nurs 2004;47:287–296.
- Zink W, Sinner B, Zausig Y, Graf BM: [Myotoxicity of local anaesthetics: experimental myth or clinical truth?]. Anaesthesist 2007;56:118–127.
- Perez-Castro R, Patel S, Garavito-Aguilar ZV et al: Cytotoxicity of local anesthetics in human neuronal cells. Anesth Analg 2009;108:997–1007.
- Radwan IA, Saito S, Goto F: The neurotoxicity of local anesthetics on growing neurons: a comparative study of lidocaine, bupivacaine, mepivacaine, and ropivacaine. Anesth Analg 2002;94:319–324, table of contents.
- Farber SJ, Saheb-Al-Zamani M, Zieske L, et al: Peripheral nerve injury after local anesthetic injection. Anesth Analg 2013;117:731–739.
- Lirk P, Haller I, Myers RR, et al: Mitigation of direct neurotoxic effects of lidocaine and amitriptyline by inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in vitro and in vivo. Anesthesiology 2006;104:1266–1273.
- Yang S, Abrahams MS, Hurn PD, Grafe MR, Kirsch JR: Local anesthetic Schwann cell toxicity is time and concentration dependent. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2011;36:444–451.
- Kalichman MW: Physiologic mechanisms by which local anesthetics may cause injury to nerve and spinal cord. Reg Anesth 1993;18:448–452.
- Gentili F, Hudson AR, Hunter D, Kline DG: Nerve injection injury with local anesthetic agents: a light and electron microscopic, fluorescent microscopic, and horseradish peroxidase study. Neurosurgery 1980;6:263–272.
- Farber SJ, Saheb-Al-Zamani M, Zieske L, et al: Peripheral nerve injury after local anesthetic injection. Anesth Analg 2013;117:731–739.
- Ahn KS, Kopp SL, Watson JC, Scott KP, Trousdale RT, Hebl JR: Postsurgical inflammatory neuropathy. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2011;36: 403–405.
- Staff NP, Engelstad J, Klein CJ, et al: Post-surgical inflammatory neuropathy. Brain 2010;133:2866–2880.
- Kaufman MR, Elkwood AI, Rose MI, et al: Surgical treatment of permanent diaphragm paralysis after interscalene nerve block for shoulder surgery. Anesthesiology 2013;119:484–487.
- Pintaric TS, Cvetko E, Strbenc M, Mis K, Podpecan O, Mars T, Hadzic A. Intraneural and perineural inflammatory changes in piglets after injection of ultrasound gel, endotoxin, 0.9% NaCl, or needle insertion without injection. Anesth Analg 2014;118(4):869–873.
- Pintaric TS, Hadzic A, Strbenc M, Podpecan O, Podbregar M, Cvetko E. Inflammatory response after injection of aqueous gel into subarachnoid space in piglets. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2013;38(2):100–105.
- Welch MB, Brummett CM, Welch TD, et al: Perioperative peripheral nerve injuries: a retrospective study of 380,680 cases during a 10-year period at a single institution. Anesthesiology 2009;111:490–497.
- Jacob AK, Mantilla CB, Sviggum HP, Schroeder DR, Pagnano MW,
Hebl JR: Perioperative nerve injury after total knee arthroplasty: regional anesthesia risk during a 20-year cohort study. Anesthesiology 2011;114: 311–317. - Jacob AK, Mantilla CB, Sviggum HP, Schroeder DR, Pagnano MW,
Hebl JR: Perioperative nerve injury after total hip arthroplasty: regional anesthesia risk during a 20-year cohort study. Anesthesiology 2011;115: 1172–1178. - Sviggum HP, Jacob AK, Mantilla CB, Schroeder DR, Sperling JW,
Hebl JR: Perioperative nerve injury after total shoulder arthroplasty: assessment of risk after regional anesthesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2012;37:490–494. - Lenters TR, Davies J, Matsen FA 3rd: The types and severity of complications associated with interscalene brachial plexus block anesthesia: local and national evidence. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2007;
16:379–387. - Widmer B, Lustig S, Scholes CJ, et al: Incidence and severity of complications due to femoral nerve blocks performed for knee surgery. Knee 2013;20:181–185.
- Hogan QH: Phrenic nerve function after interscalene block revisited: now, the long view. Anesthesiology 2013;119:250–252.
- Gadsden J, Gratenstein K, Hadzic A: Intraneural injection and peripheral nerve injury. Int Anesthesiol Clin 2010;48:107–115.
- Liu SS, YaDeau JT, Shaw PM, Wilfred S, Shetty T, Gordon M: Incidence of unintentional intraneural injection and postoperative neurological complications with ultrasound-guided interscalene and supraclavicular nerve blocks. Anaesthesia 2011;66:168–174.
- Bigeleisen PE: Nerve puncture and apparent intraneural injection during ultrasound-guided axillary block does not invariably result in neurologic injury. Anesthesiology 2006;105:779–783.
- Bigeleisen PE, Moayeri N, Groen GJ: Extraneural versus intraneural stimulation thresholds during ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block. Anesthesiology 2009;110:1235–1243.
- Sala Blanch X, Lopez AM, Carazo J, et al: Intraneural injection during nerve stimulator-guided sciatic nerve block at the popliteal fossa. Br J Anaesth 2009;102:855–861.
- Cohen JM, Gray AT: Functional deficits after intraneural injection during interscalene block. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2010;35:397–399.
- Orebaugh SL, McFadden K, Skorupan H, Bigeleisen PE: Subepineurial injection in ultrasound-guided interscalene needle tip placement. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2010;35:450–454.
- Altermatt FR, Cummings TJ, Auten KM, Baldwin MF, Belknap SW, Reynolds JD: Ultrasonographic appearance of intraneural injections in the porcine model. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2010;35:203–206.
- Moayeri N, Bigeleisen PE, Groen GJ: Quantitative architecture of the brachial plexus and surrounding compartments, and their possible significance for plexus blocks. Anesthesiology 2008;108:299–304.
- Moayeri N, Groen GJ: Differences in quantitative architecture of sciatic nerve may explain differences in potential vulnerability to nerve injury, onset time, and minimum effective anesthetic volume. Anesthesiology 2009;111:1128–1134.
- Borgeat A, Ekatodramis G, Kalberer F, Benz C: Acute and nonacute complications associated with interscalene block and shoulder surgery: a prospective study. Anesthesiology 2001;95:875–880.
- Candido KD, Sukhani R, Doty R Jr, et al: Neurologic sequelae after interscalene brachial plexus block for shoulder/upper arm surgery: the association of patient, anesthetic, and surgical factors to the incidence and clinical course. Anesth Analg 2005;100:1489–1495, table of contents.
- Bilbao Ares A, Sabate A, Porteiro L, Ibanez B, Koo M, Pi A: [Neurological complications associated with ultrasound-guided interscalene and supraclavicular block in elective surgery of the shoulder and arm. Prospective observational study in a university hospital.]. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim 2013;60:384–391.
- Auroy Y, Benhamou D, Bargues L, et al: Major complications of regional anesthesia in France: The SOS Regional Anesthesia Hotline Service. Anesthesiology 2002;97:1274–1280.
- Barrington MJ, Watts SA, Gledhill SR, et al: Preliminary results of the Australasian Regional Anaesthesia Collaboration: a prospective audit of more than 7000 peripheral nerve and plexus blocks for neurologic and other complications. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2009;34:534–541.
- Fanelli G, Casati A, Garancini P, Torri G: Nerve stimulator and multiple injection technique for upper and lower limb block: failure rate, patient acceptance, and neurologic complications. Study Group on Regional Anesthesia. Anesth Analg 1999;88:847–852.
- Selander D, Dhuner KG, Lundborg G: Peripheral nerve injury due to injection needles used for regional anesthesia. An experimental study of the acute effects of needle point trauma. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1977;21:182–188.
- Steinfeldt T, Nimphius W, Werner T, et al: Nerve injury by needle nerve perforation in regional anaesthesia: does size matter? Br J Anaesth 2010;104:245–253.
- Steinfeldt T, Werner T, Nimphius W, et al: Histological analysis after peripheral nerve puncture with pencil-point or Tuohy needletip. Anesth Analg 2011;112:465–470.
- Reina MA, de Leon-Casasola OA, Lopez A, De Andres J, Martin S, Mora M: An in vitro study of dural lesions produced by 25-gauge Quincke and Whitacre needles evaluated by scanning electron microscopy. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2000;25:393–402.
- Selander D: Peripheral nerve injury caused by injection needles. Br J Anaesth 1993;71:323–325.
- Selander DE: Labat lecture 2006. Regional anesthesia: aspects, thoughts, and some honest ethics; about needle bevels and nerve lesions, and back pain after spinal anesthesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2007;32:341–350.
- Winfree CJ, Kline DG: Intraoperative positioning nerve injuries. Surg Neurol 2005;63:5–18; discussion 18.
- Kroll DA, Caplan RA, Posner K, Ward RJ, Cheney FW: Nerve injury
associated with anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1990;73:202–207. - Jankowski CJ, Keegan MT, Bolton CF, Harrison BA: Neuropathy following axillary brachial plexus block: is it the tourniquet? Anesthesiology 2003;99:1230–1232.
- Kornbluth ID, Freedman MK, Sher L, Frederick RW: Femoral, saphenous nerve palsy after tourniquet use: a case report. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2003;84:909–911.
- Maguina P, Jean-Pierre F, Grevious MA, Malk AS: Posterior interosseous branch palsy following pneumatic tourniquet application for hand surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 2008;122:97e–99e.
- Barner KC, Landau ME, Campbell WW: A review of perioperative nerve injury to the lower extremities: part I. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 2002;4: 95–99.
- Nitz AJ, Dobner JJ, Matulionis DH: Structural assessment of rat sciatic nerve following tourniquet compression and vascular manipulation. Anat Rec 1989;225:67–76.
- Dobner JJ, Nitz AJ: Postmeniscectomy tourniquet palsy and functional sequelae. Am J Sports Med 1982;10:211–214.
- Weingarden SI, Louis DL, Waylonis GW: Electromyographic changes in postmeniscectomy patients. Role of the pneumatic tourniquet. JAMA 1979;241:1248–1250.
- Fabre T, Piton C, Andre D, Lasseur E, Durandeau A: Peroneal nerve entrapment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1998;80:47–53.
- Prielipp RC, Warner MA: Perioperative nerve injury: a silent scream? Anesthesiology 2009;111:464–466.
- Warner MA, Warner ME, Martin JT: Ulnar neuropathy. Incidence, outcome, and risk factors in sedated or anesthetized patients. Anesthesiology 1994;81:1332–1340.
- Morales-Vidal S, Morgan C, McCoyd M, Hornik A: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Postgrad Med 2012;124:145–153.
- Kalichman MW, Calcutt NA: Local anesthetic-induced conduction block and nerve fiber injury in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Anesthesiology 1992;77:941–947.
- Hebl JR, Kopp SL, Schroeder DR, Horlocker TT: Neurologic complications after neuraxial anesthesia or analgesia in patients with preexisting peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy or diabetic polyneuropathy. Anesth Analg 2006;103:1294–1299.
- Neal JM, Bernards CM, Hadzic A, et al: ASRA Practice Advisory on Neurologic Complications in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2008;33:404–415.
- Mellion M, Gilchrist JM, de la Monte S: Alcohol-related peripheral neuropathy: nutritional, toxic, or both? Muscle Nerve 2011;43: 309–316.
- Hebl JR, Horlocker TT, Pritchard DJ: Diffuse brachial plexopathy after interscalene block in a patient receiving cisplatin chemotherapy: the pharmacologic double crush syndrome. Anesth Analg 2001;92:249–251.
- Hebl JR: Ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia and the prevention of neurologic injury: fact or fiction? Anesthesiology 2008;108:186–188.
- Uskova AA, Plakseychuk A, Chelly JE: The role of surgery in postoperative nerve injuries following total hip replacement. J Clin Anesth 2010;22: 285–293.
- Moen V, Dahlgren N, Irestedt L: Severe neurological complications after central neuraxial blocks in Sweden 1990–1999. Anesthesiology 2004;101:950–959.
- Kubina P, Gupta A, Oscarsson A, Axelsson K, Bengtsson M: Two cases of cauda equina syndrome following spinal-epidural anesthesia. Reg Anesth 1997;22:447–450.
- Hebl JR, Horlocker TT, Kopp SL, Schroeder DR: Neuraxial block in patients with preexisting spinal stenosis, lumbar disk disease, or prior spine surgery: efficacy and neurologic complications. Anesth Analg
2010;111:1511–1519. - Barner KC, Landau ME, Campbell WW: A review of perioperative nerve injury to the upper extremities. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 2003;4: 117–123.
- Sunderland S: The relative susceptibility to injury of the medial and lateral popliteal divisions of the sciatic nerve. Br J Surg 1953;41:300–302.
- Sunderland S: The sciatic nerve and its tibial and common peroneal divisions. Anatomical and physiological features. Nerves and Nerve Injuries, Churchill Livingstone, 1978, pp 924–966.
- Bernards CM, Hadzic A, Suresh S, Neal JM: Regional anesthesia in anesthetized or heavily sedated patients. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2008;33: 449–460.
- Nitz AJ, Dobner JJ, Matulionis DH: Pneumatic tourniquet application and nerve integrity: motor function and electrophysiology. Exp Neurol 1986;94:264–279.
- Horlocker TT, Cabanela ME, Wedel DJ: Does postoperative epidural analgesia increase the risk of peroneal nerve palsy after total knee arthroplasty? Anesth Analg 1994;79:495–500.
- Sala-Blanch X, Lopez AM, Carazo J, et al: Intraneural injection during nerve stimulator-guided sciatic nerve block at the popliteal fossa. Br J Anaesth 2009;102:855–861.
- Jeng CL, Rosenblatt MA: Intraneural injections and regional anesthesia: the known and the unknown. Minerva Anestesiol 2011;77:54–58.
- Moore DC: “No paresthesias-no anesthesia,” the nerve stimulator or neither? Reg Anesth 1997;22:388–390.
- Auroy Y, Narchi P, Messiah A, Litt L, Rouvier B, Samii K: Serious complications related to regional anesthesia: results of a prospective survey in France. Anesthesiology 1997;87:479–486.
- Winchell SW, Wolfe R: The incidence of neuropathy following upper extremity nerve blocks. Reg Anesth Pain Med 1985;10:12–15.
- Urban MK, Urquhart B: Evaluation of brachial plexus anesthesia for upper extremity surgery. Reg Anesth 1994;19:175–182.
- Liguori GA, Zayas VM, YaDeau JT, et al: Nerve localization techniques for interscalene brachial plexus block: a prospective, randomized comparison of mechanical paresthesia versus electrical stimulation. Anesth Analg 2006;103:761–767.
- Perlas A, Niazi A, McCartney C, Chan V, Xu D, Abbas S: The sensitivity of motor response to nerve stimulation and paresthesia for nerve localization as evaluated by ultrasound. Reg Anesth Pain Med
2006;31:445–450. - Klein SM, Melton MS, Grill WM, Nielsen KC: Peripheral nerve stimulation in regional anesthesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2012;37: 383–392.
- Voelckel WG, Klima G, Krismer AC, et al: Signs of inflammation after sciatic nerve block in pigs. Anesth Analg 2005;101:1844–1846.
- Chan VW, Brull R, McCartney CJ, Xu D, Abbas S, Shannon P: An ultrasonographic and histological study of intraneural injection and electrical stimulation in pigs. Anesth Analg 2007;104:1281–1284, table of contents.
- Tsai TP, Vuckovic I, Dilberovic F, et al: Intensity of the stimulating current may not be a reliable indicator of intraneural needle placement. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2008;33:207–210.
- Robards C, Hadzic A, Somasundaram L, et al: Intraneural injection with low-current stimulation during popliteal sciatic nerve block. Anesth Analg 2009;109:673–677.
- Reiss W, Kurapati S, Shariat A, Hadzic A: Nerve injury complicating ultrasound/electrostimulation-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2010;35:400–401.
- Urmey WF, Stanton J: Inability to consistently elicit a motor response following sensory paresthesia during interscalene block administration. Anesthesiology 2002;96:552–554.
- Watts SA: Long-term neurological complications associated with surgery and peripheral nerve block: outcomes after 1065 consecutive blocks. Anaesth Intensive Care 2007;35:24–31.
- Orebaugh SL, Williams BA, Vallejo M, Kentor ML: Adverse outcomes associated with stimulator-based peripheral nerve blocks with versus without ultrasound visualization. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2009;34: 251–255.
- Selander D, Brattsand R, Lundborg G, Nordborg C, Olsson Y: Local anesthetics: importance of mode of application, concentration and adrenaline for the appearance of nerve lesions. An experimental study of axonal degeneration and barrier damage after intrafascicular injection or topical application of bupivacaine (Marcain). Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1979;23:127–136.
- Kapur E, Vuckovic I, Dilberovic F, et al: Neurologic and histologic outcome after intraneural injections of lidocaine in canine sciatic nerves. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2007;51:101–107.
- Lupu CM, Kiehl TR, Chan VW, El-Beheiry H, Madden M, Brull R: Nerve expansion seen on ultrasound predicts histologic but not functional nerve injury after intraneural injection in pigs. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2010;35:132–139.
- Orebaugh SL, Mukalel JJ, Krediet AC, et al: Brachial plexus root injection in a human cadaver model: injectate distribution and effects on the neuraxis. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2012;37:525–529.
- Andrzej Krol, Matthew Szarko, Arber Vala, Jose De Andres: Pressure Monitoring of Intraneural an Perineural Injections Into the Median, Radial, and Ulnar Nerves; Lessons From a Cadaveric Study. Anesth Pain Med. 2015 June;5(3):e22723. DOI: 10.5812/aapm.22723.
- Sala-Blanch X, de Riva N, Carrera A, Lopez AM, Prats A, Hadzic A: Ultrasound-guided popliteal sciatic block with a single injection at the sciatic division results in faster block onset than the classical nerve stimulator technique. Anesth Analg 2012;114:1121–1127.
- Sala-Blanch X, Lopez AM, Pomes J, Valls-Sole J, Garcia AI, Hadzic A: No clinical or electrophysiologic evidence of nerve injury after intraneural injection during sciatic popliteal block. Anesthesiology 2011;115:589–595.
- Gadsden JC, Lindenmuth DM, Hadzic A, Xu D, Somasundarum L, Flisinski KA: Lumbar plexus block using high-pressure injection leads to contralateral and epidural spread. Anesthesiology 2008;109:683–688.
- Tsui BC, Li LX, Pillay JJ: Compressed air injection technique to standardize block injection pressures. Can J Anaesth 2006;53:1098–1102.
- Siegmueller C, Ramessur S: A simple low-cost way of measuring injection pressure during peripheral nerve block. Anaesthesia 2011;66:956.
- Gerancher JC, Viscusi ER, Liguori GA, et al: Development of a standardized peripheral nerve block procedure note form. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2005;30:67–71.
- Claudio R, Hadzic A, Shih H, et al: Injection pressures by anesthesiologists during simulated peripheral nerve block. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2004;29: 201–205.
- Theron PS, Mackay Z, Gonzalez JG, Donaldson N, Blanco R: An animal model of “syringe feel” during peripheral nerve block. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2009;34:330–332.
- Ip VH, Tsui BC: Practical concepts in the monitoring of injection pressures during peripheral nerve blocks. Int Anesthesiol Clin 2011;49: 67–80.
- Gadsden JC, Choi JJ, Lin E, Robinson A: Opening injection pressure consistently detects needle-nerve contact during ultrasound-guided interscalene brachial plexus block. Anesthesiology 2014;120: 1246–1253.
- Tsui BC, Pillay JJ, Chu KT, Dillane D: Electrical impedance to distinguish intraneural from extraneural needle placement in porcine nerves during direct exposure and ultrasound guidance. Anesthesiology 2008;109:479–483.
- Byrne K, Tsui BC: Practical concepts in nerve stimulation: impedance and other recent advances. Int Anesthesiol Clin 2011;49:81–90.
- Sauter AR, Dodgson MS, Kalvoy H, Grimnes S, Stubhaug A, Klaastad Ø: Current threshold for nerve stimulation depends on electrical impedance of the tissue: a study of ultrasound-guided electrical nerve stimulation of the median nerve. Anesth Analg 2009;108:1338–1343.
- Sites BD, Spence BC, Gallagher JD, Wiley CW, Bertrand ML, Blike GT: Characterizing novice behavior associated with learning ultrasound-guided peripheral regional anesthesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2007;32: 107–115.
- Sites BD, Taenzer AH, Herrick MD, et al: Incidence of local anesthetic systemic toxicity and postoperative neurologic symptoms associated with 12,668 ultrasound-guided nerve blocks: an analysis from a prospective clinical registry. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2012;37:478–482.