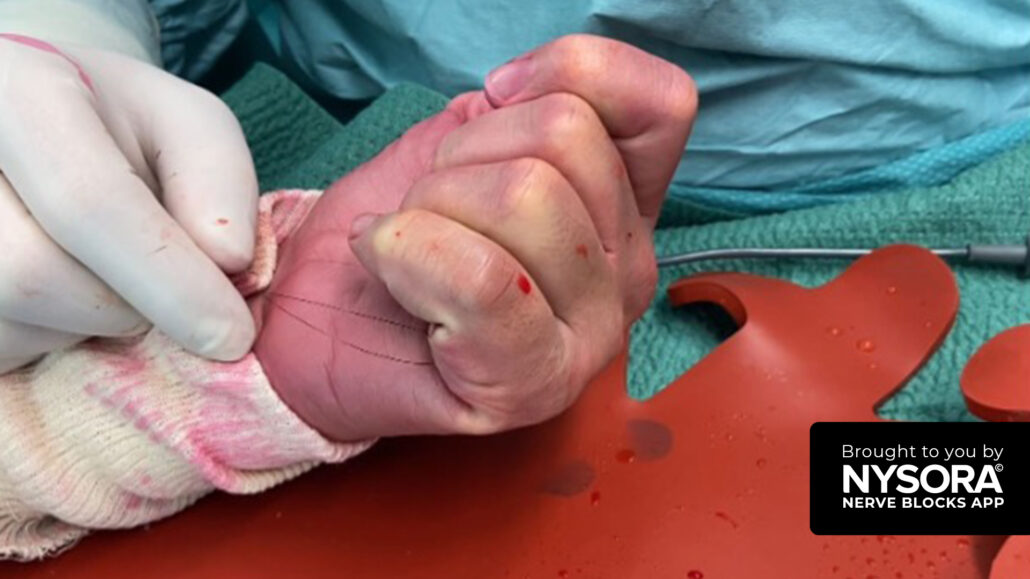
Case study: Flexor tendon release
Case presentation
A 56-year-old woman presented six weeks postoperatively from a surgical repair of a flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) laceration. She demonstrated an active flexion dysfunction of the fifth digit. Given the necessity for intraoperative patient cooperation to gauge the surgery’s functional outcome, general anesthesia was ruled out.
Nerve block techniques
Median and ulnar nerve blocks at the wrist
- Rationale: Blocking the median and ulnar nerves just proximal to the wrist crease allows for anesthesia of the fifth digit without compromising the motor function of the hand flexors. This approach ensures complete anesthesia for the surgical intervention while preserving the ability to test finger flexion actively.
- Technique: Under ultrasound guidance, the median and ulnar nerves were identified between the superficial and deep flexors of the wrist and fingers. Next, a 25-gauge needle was inserted in-plane or out-of-plane to inject 5 mL of lidocaine 2% into the fascia containing the nerves. The onset of anesthesia was observed within 10 minutes.
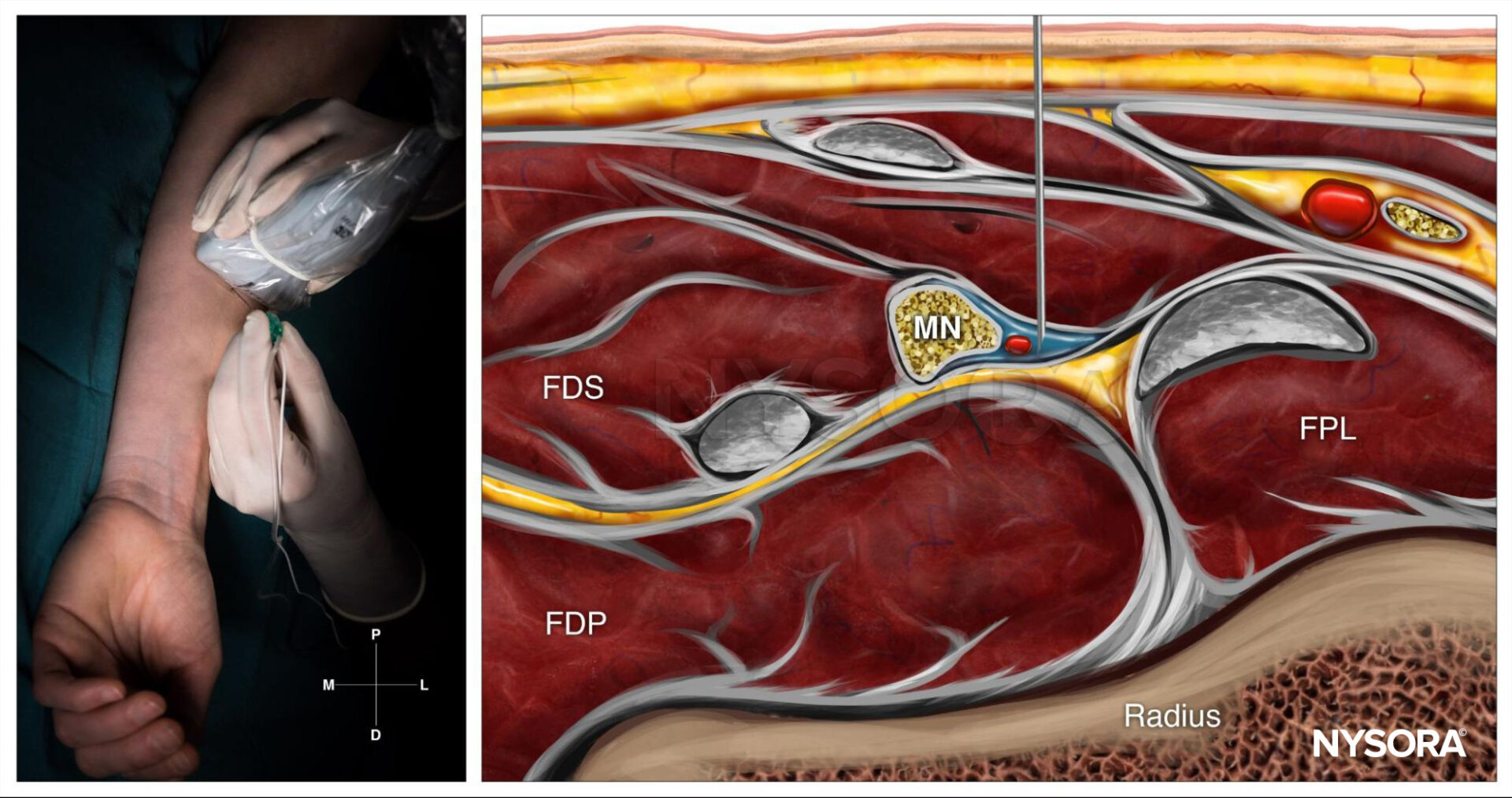
Median nerve block at the level of the wrist; Reverse Ultrasound Anatomy with needle insertion out-of-plane and local anesthetic spread (blue). MN, median nerve; FPL, flexor pollicis longus muscle; FDS, flexor digitorum superficialis muscle; FDP, flexor digitorum profundus muscle.
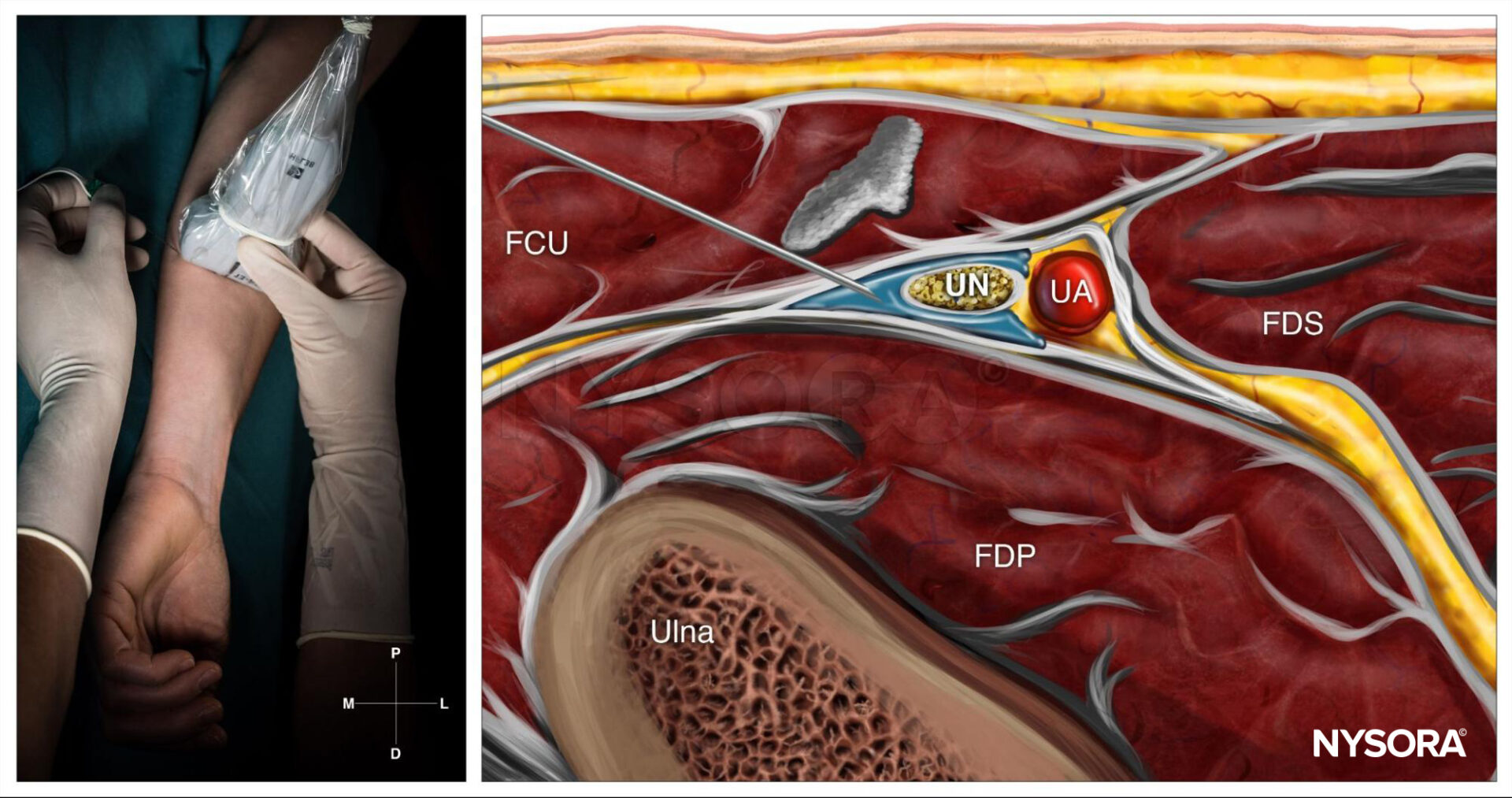
Ulnar nerve block at the level of the wrist; Reverse Ultrasound Anatomy with needle insertion in-plane and local anesthetic spread (blue). UN, ulnar nerve; UA, ulnar artery; FCU, flexor carpi ulnaris; FDP, flexor digitorum profundus muscle; FDS, flexor digitorum superficialis muscle.
Patient outcome
Throughout the surgical procedure, the patient was comfortable and pain-free, confirming the nerve blocks’ effectiveness. The patient could actively open and close her hand upon the surgeon’s request, allowing real-time assessment of the fifth digit’s flexor tendon. Although the tendon release initially seemed successful, further intraoperative testing revealed residual adhesions. The surgeon then undertook additional cleaning of the flexor tendon, achieving a complete restoration of hand function.
For more case studies like these and the complete guide to the 60 most frequently used nerve blocks, download the Nerve Blocks App HERE. Don’t miss the chance to get the bestselling NYSORA Nerve Blocks App also in book format – the perfect study companion with the Nerve Blocks app!