股神经阻滞的技巧
2024 年 3 月 26 日
股神经阻滞是临床应用最广泛、成功率较高的神经阻滞技术之一。超声引导技术允许医生监测局部麻醉剂的扩散和针的放置,进行调整,并降低股动脉穿刺的风险。
与更远端的技术(例如股骨三角阻滞或内收肌管阻滞)相反,股神经阻滞可以为膝关节手术提供完全麻醉。
遵循以下 3 个成功股神经阻滞的基本技巧:
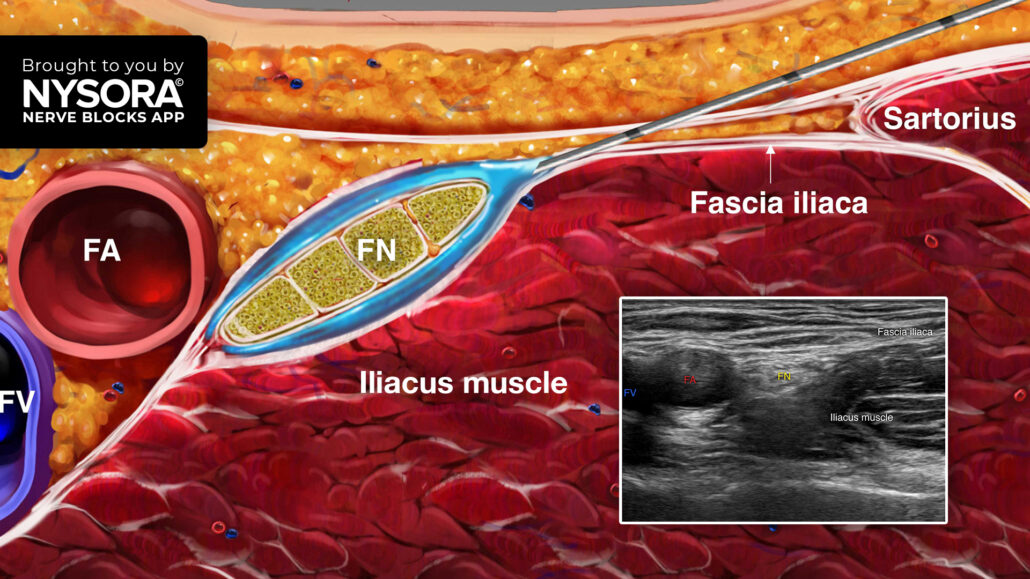
- 将换能器横向放置在股骨折痕上。
- 识别股动脉及其内侧的股静脉。
- 平面内进针,从外侧到内侧,刺穿股神经外侧的髂筋膜,注入局麻药 10-15 mL。
观看下面的视频以更好地了解该过程并了解如何 NYSORA 神经阻滞应用程序 将这些指示变为现实:
如需更多此类提示以及 60 种最常用神经阻滞的完整指南,请下载 Nerve Blocks App 点击这里。 不要错过获得最畅销的 NYSORA 神经阻滞应用程序的机会 书本格式 – Nerve Blocks 应用程序的完美学习伴侣!