Explore NYSORA knowledge base for free:
Get yours now and be on the cutting edge of regional anesthesia!
This app is ideal for anesthesiology and pain professionals seeking a comprehensive, on-the-go knowledge base for ultrasound-guided nerve blocks and fascial plane blocks.
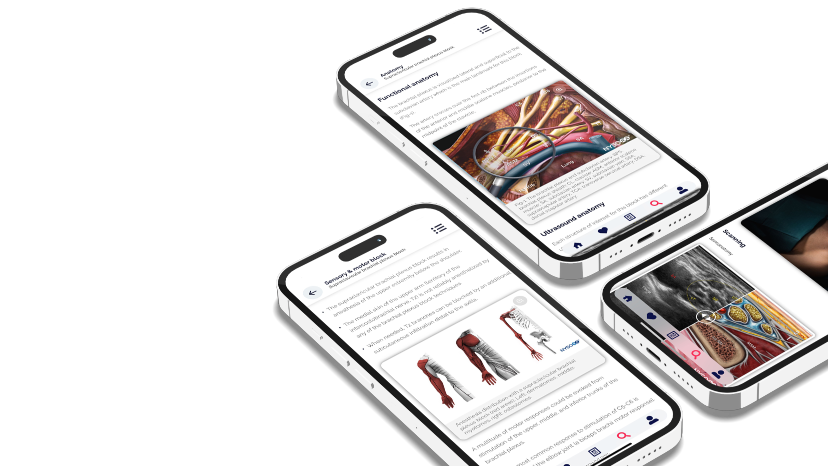
Download the NYSORA Nerve Blocks app today and test drive the free blocks!
Cervical plexus block
Sub-Tenon’s (episcleral) eye block
Retrobulbar eye block
Peribulbar eye block
Interscalene brachial plexus block
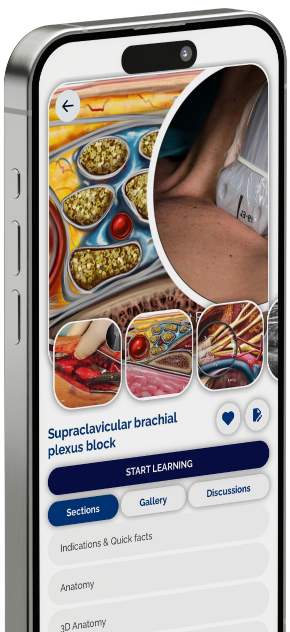
Supraclavicular brachial plexus block
Infraclavicular brachial plexus block
Costoclavicular brachial plexus
Shoulder block
Axillary brachial plexus block
Nerve blocks above the elbow
Wrist block
Fascia iliaca block – infrainguinal approach
Fascia iliaca block – suprainguinal approach
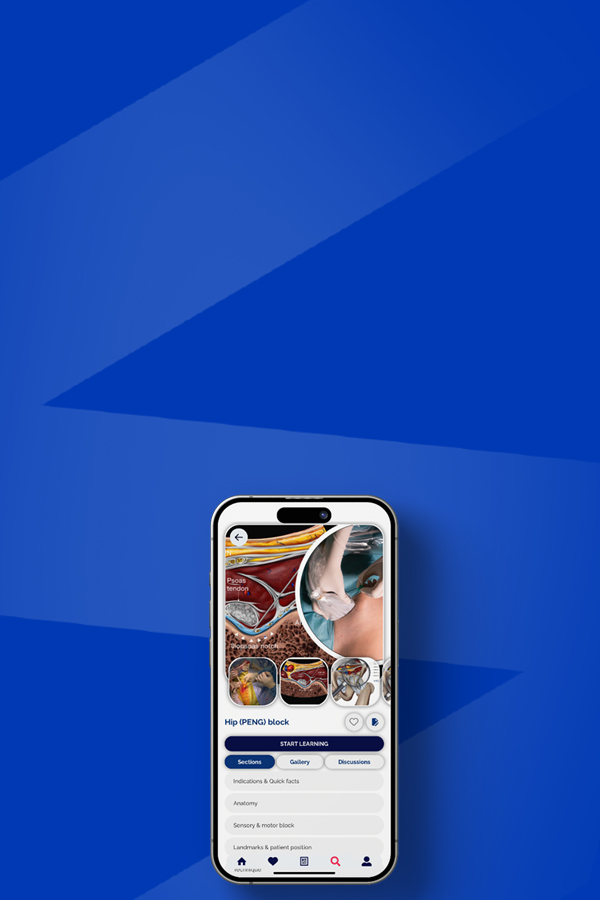
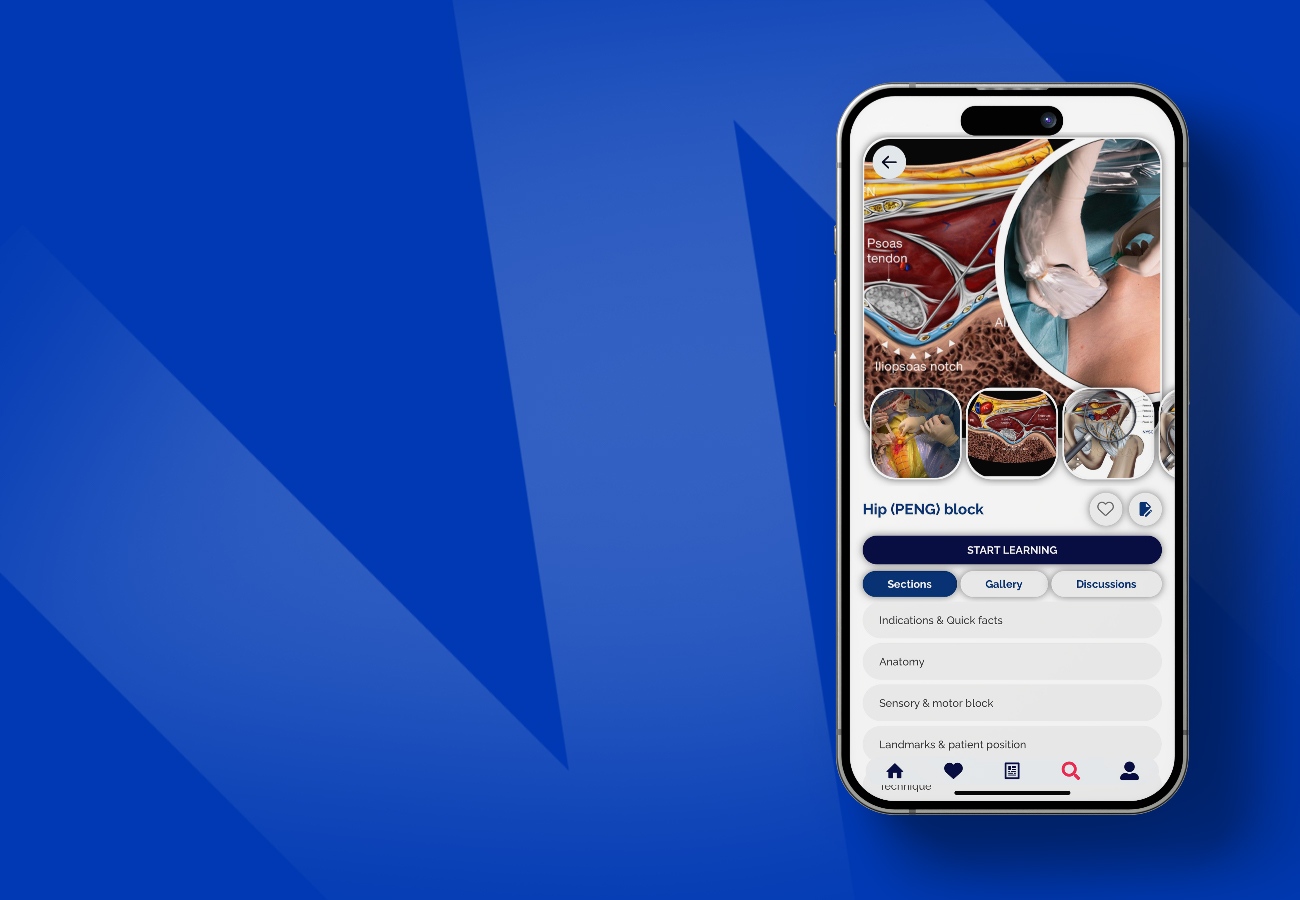
Hip (PENG) block
Femoral nerve block
Adductor canal block (saphenous nerve)
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve block
Obturator nerve block
Proximal sciatic nerve block
Popliteal sciatic nerve block
Genicular nerve block
IPACK block
Ankle block
Intercostal nerve block
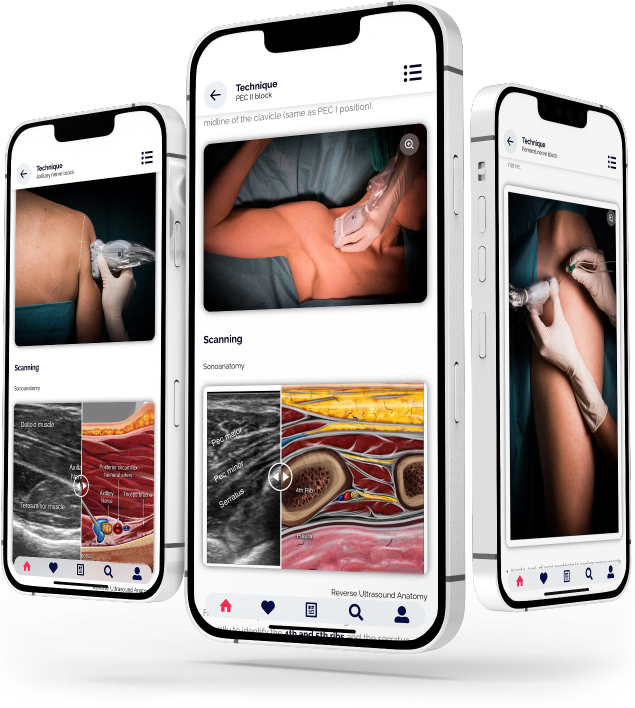
Pectoralis and serratus plane blocks
Paravertebral block
Transversus abdominis plane
(TAP) blocks
Quadratus lumborum (QL) blocks
Erector spinae plane (ESP) block
Rectus sheath block
Regional anesthesia numbs a specific area of the body, blocking pain in that region during and after surgical procedures. Unlike general anesthesia, which renders the patient unconscious, regional anesthesia allows the patient to remain awake or lightly sedated without feeling pain in the targeted area. This is achieved by inhibiting the transmission of pain signals to the brain.
Regional anesthesia has several benefits, such as minimized systemic opioid requirements, reduced postoperative pain and nausea, and improved recovery rates. It also decreases the risk of complications associated with general anesthesia, making it a preferred choice for specific patient populations and surgical interventions. Additionally, it can provide pain relief for several hours or days after the procedure.
Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks are a medical procedure used to alleviate pain by targeting specific nerves by administering local anesthetics or other therapeutic agents. Ultrasound imaging visualizes the nerves and surrounding structures in real-time, allowing for precise needle placement and injection.
Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks provide numerous advantages. They intensify accuracy and precision by enabling clear visualization of the targeted nerve and surrounding structures, minimizing the likelihood of errors in needle placement. This increases the efficacy of the procedure but also reduces the risk of complications such as inadvertent vascular puncture or nerve damage. Furthermore, the real-time visualization with ultrasound allows for immediate adjustments during needle placement, optimizing the delivery of medication and ensuring its effective localization.
Nerve blocks offer precise pain control in specific regions of the body for surgical procedures, trauma management, and pain interventions. By delivering anesthesia directly to the site of action, nerve blocks minimize systemic side effects associated with general anesthesia, improving patient safety and comfort. They can also reduce the need for general anesthesia, leading to shorter hospital stays, decreased opioid consumption, earlier mobilization, and faster recovery times. Moreover, these nerve blocks enhance surgical conditions by providing optimal anesthesia to the surgical site, thereby improving surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
The NYSORA Nerve Blocks App is designed to cater to a diverse global audience, ensuring that healthcare professionals worldwide can access its comprehensive educational content on nerve block techniques. As of the latest update, the app is available in multiple languages, including English, Spanish, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, French, Dutch, and German. This multilingual support underscores NYSORA's commitment to promoting excellence in regional anesthesia and pain management across different linguistic and cultural backgrounds.